The CEO’s Guide to Business Model Innovation
This article discusses slides taken from a strategy consulting presentation on Business Model Innovation. You can download the full PPT here.
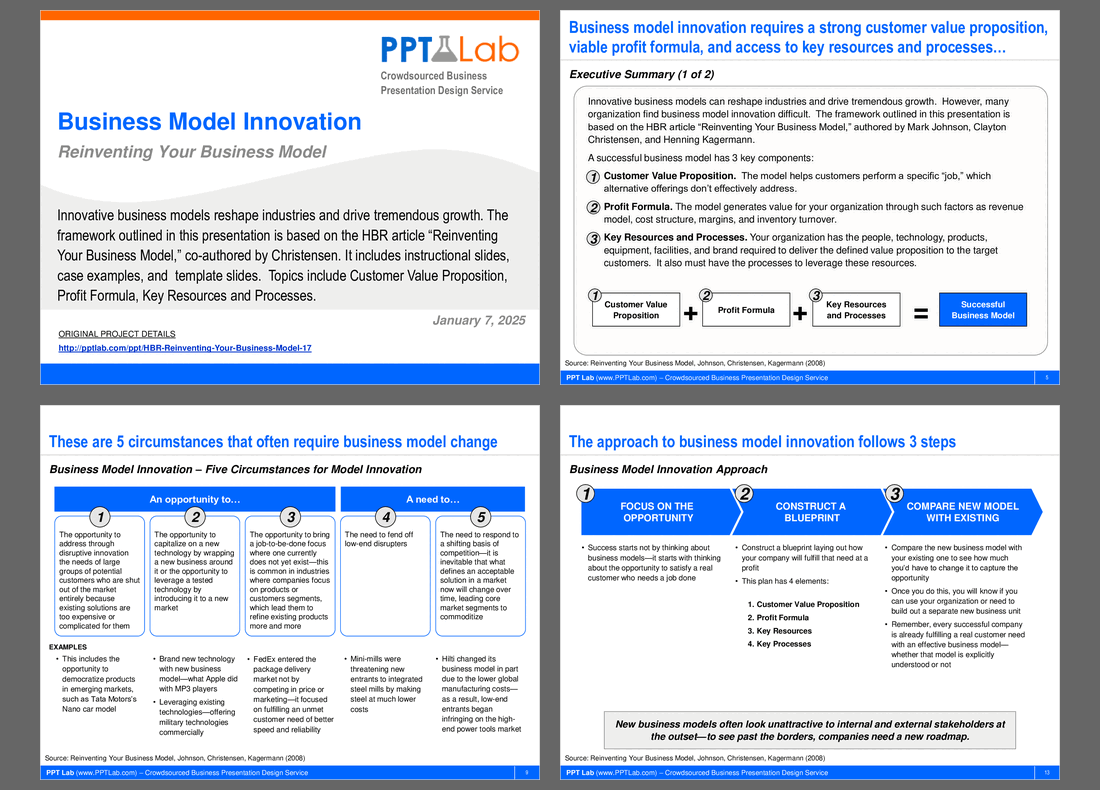
The presentation focuses on the critical topic of business model innovation, emphasizing its potential to transform industries and drive significant growth. Despite widespread recognition of its importance, many organizations struggle with effective implementation, often falling prey to common pitfalls that hinder their progress.
It introduces a structured framework based on the principles outlined in the HBR article “Reinventing Your Business Model.” This framework highlights 3 essential components: a clear customer value proposition, a viable profit formula, and the effective use of key resources and processes. The document provides practical tools, including case examples and templates, to facilitate understanding and application, while underscoring the need for patience and adaptability throughout the innovation journey.
Key Circumstances Necessitating Business Model Innovation
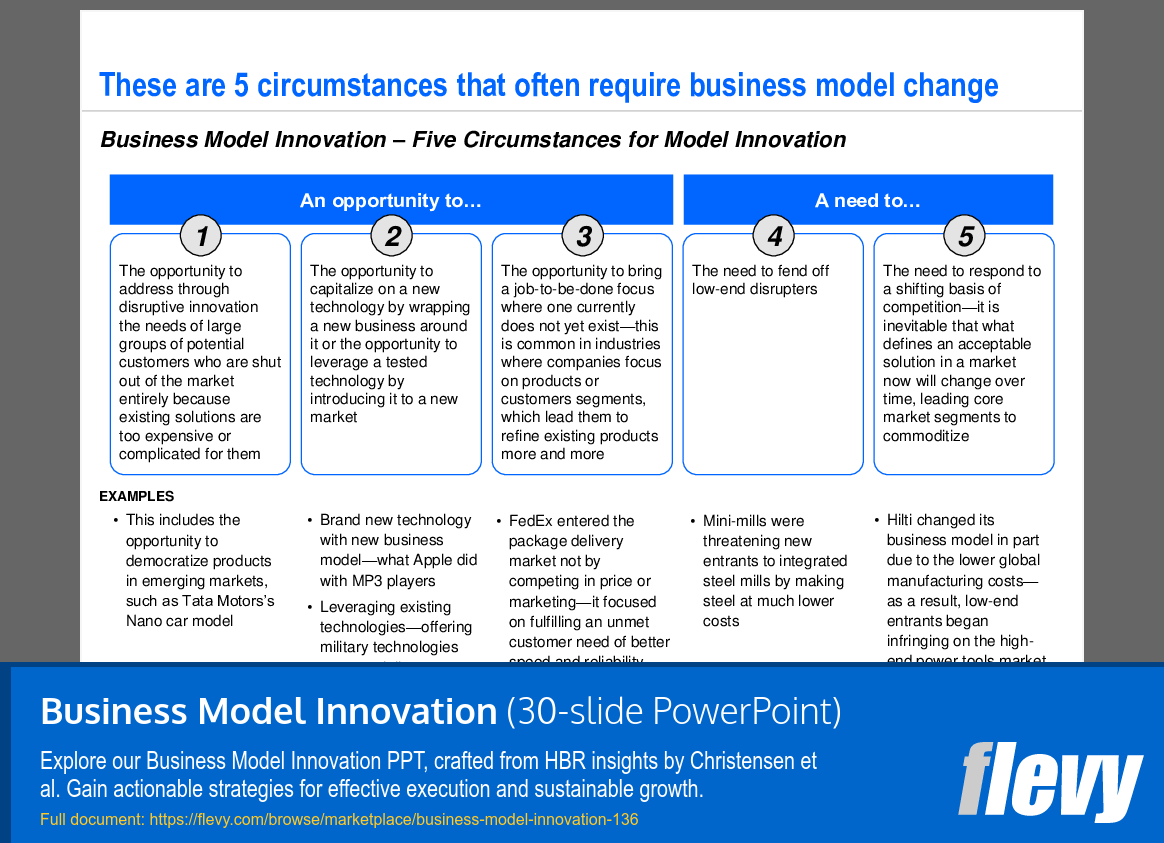
The slide identifies 5 key circumstances that prompt businesses to reconsider their models, highlighting the necessity for innovation in a changing market environment. It categorizes these circumstances into opportunities and needs, providing a clear framework for executives to assess when model innovation is warranted.
The first circumstance addresses disruptive innovations targeting large customer segments that find current solutions inadequate. Examples like Tata Motors’ Nano car illustrate how simplifying offerings can tap into new markets. The second circumstance emphasizes leveraging new technologies, as seen with Apple’s MP3 players, which can redefine consumer expectations.
The slide also discusses the importance of a job-to-be-done focus, as demonstrated by FedEx’s customer-centric approach. It warns against low-end disruptors, using mini-mills in the steel industry as a cautionary example. Lastly, it stresses the need to adapt to evolving market definitions, as illustrated by Hilti’s response to changing manufacturing costs, which allowed new entrants to gain traction.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Three-Step Framework for Business Model Innovation

The slide presents a structured approach to business model innovation, highlighting 3 essential steps. The first step emphasizes the need to identify genuine customer needs rather than focusing solely on existing business models. This customer-centric perspective is crucial for ensuring that any new model effectively addresses real demands in the market.
The second step involves constructing a detailed blueprint that outlines how the organization will meet these identified needs while maintaining profitability. This blueprint consists of 4 key components: Customer Value Proposition, Profit Formula, Key Resources, and Key Processes. Each element is integral to developing a coherent strategy that aligns with market expectations.
The final step requires a thorough comparison of the proposed business model with the existing one. This analysis helps determine the necessary changes to effectively capture the identified opportunity and assesses whether the current organization can adapt or if a new business unit is needed. Ultimately, successful companies fulfill customer needs through effective business models, regardless of their complexity or clarity.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Framework for Defining Customer Value and Profitability
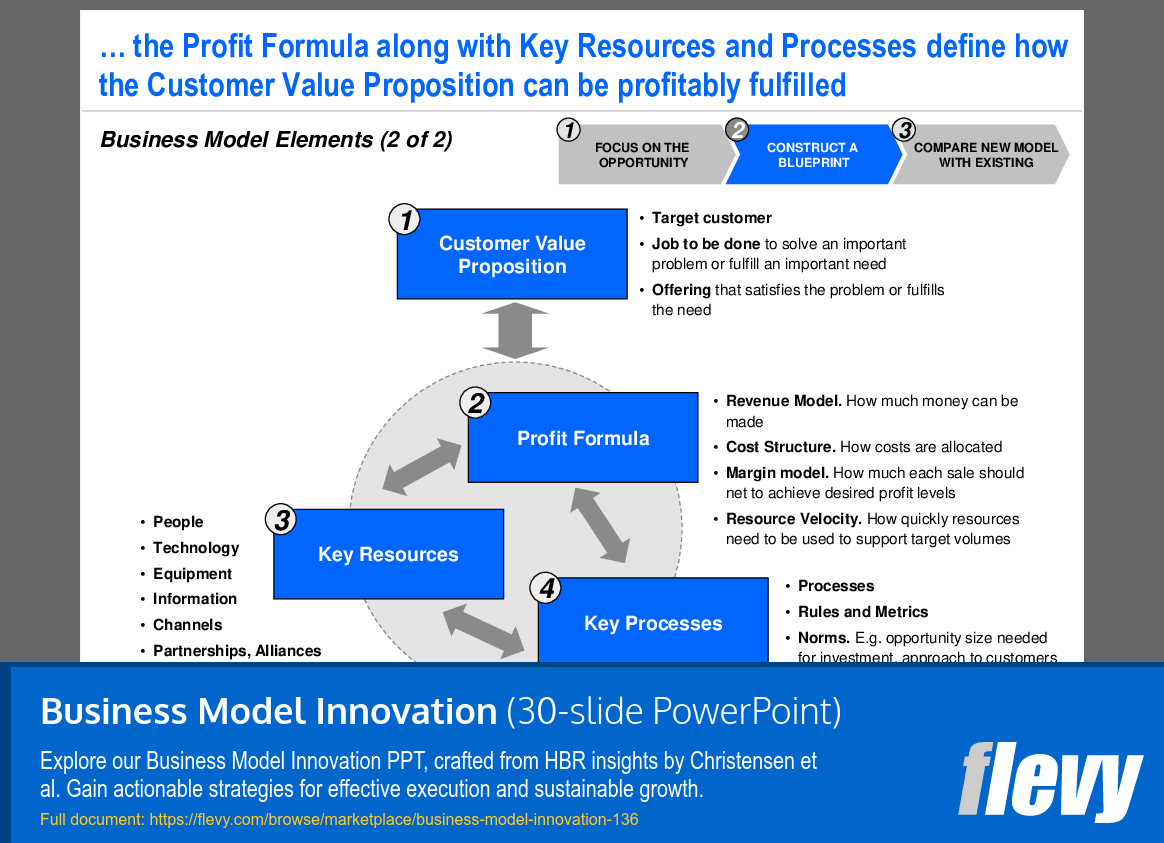
The slide presents a framework for understanding the components of a business model, focusing on how the profit formula, key resources, and key processes shape the customer value proposition. At its core, the customer value proposition hinges on identifying the target customer, understanding their needs, and providing a suitable solution. This is essential for addressing real problems and fulfilling significant market demands.
The profit formula is a critical element, detailing revenue generation, cost allocation, and the margin model necessary for achieving profit targets. Understanding these financial mechanics is vital for sustainable operations. Key resources are categorized into various areas such as people, technology, and partnerships, highlighting the diverse assets needed to effectively deliver on the value proposition.
Key processes encompass the rules and metrics that guide operational efficiency, including investment criteria and resource alignment with strategic goals. This comprehensive approach illustrates how different components interconnect to create value and drive profitability, offering a blueprint for executives aiming to innovate or refine their business strategies.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Identifying Institutional Barriers to Business Model Innovation

This slide highlights the institutional barriers that obstruct the adoption of new business models within organizations. It points out how entrenched rules, norms, and metrics can obscure the core understanding of a business model, making it challenging to integrate innovative approaches. These barriers are deeply embedded in the organizational culture and operational practices, leading to significant resistance against change.
The slide categorizes these barriers into 3 areas: Financial, Operational, and Other. Financial metrics like gross margins and unit pricing often dictate decision-making, while operational factors such as end-product quality and customer service reflect the importance of maintaining existing standards. The Other category includes broader considerations like pricing strategies and performance demands, which can complicate the process of innovation.
Ultimately, these institutionalized rules and metrics can lead to stagnation, hindering an organization’s ability to adapt in a rapidly changing environment. Recognizing and understanding these barriers is essential for any company aiming to innovate effectively.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Integrating Key Resources and Processes for Value Delivery

The slide emphasizes the importance of key resources and processes in delivering value propositions to customers. Key resources include essential assets like personnel, technology, and brand, which are crucial for meeting customer needs. The focus is on identifying elements that generate value for both the organization and its customers.
Key processes are operational and managerial practices that allow companies to consistently deliver value. These processes are recurrent and span various functions, such as training and sales. Successful organizations uniquely integrate their resources and processes to effectively serve their target markets, with examples showing how different industries prioritize distinct elements.
Aligning the value proposition with the profit formula is critical for creating a sustainable business model. The slide also highlights that rules and metrics often develop later, underscoring the need for flexibility during the early stages of a business model’s evolution.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Transforming Business Models: Dow Corning’s Strategic Shift
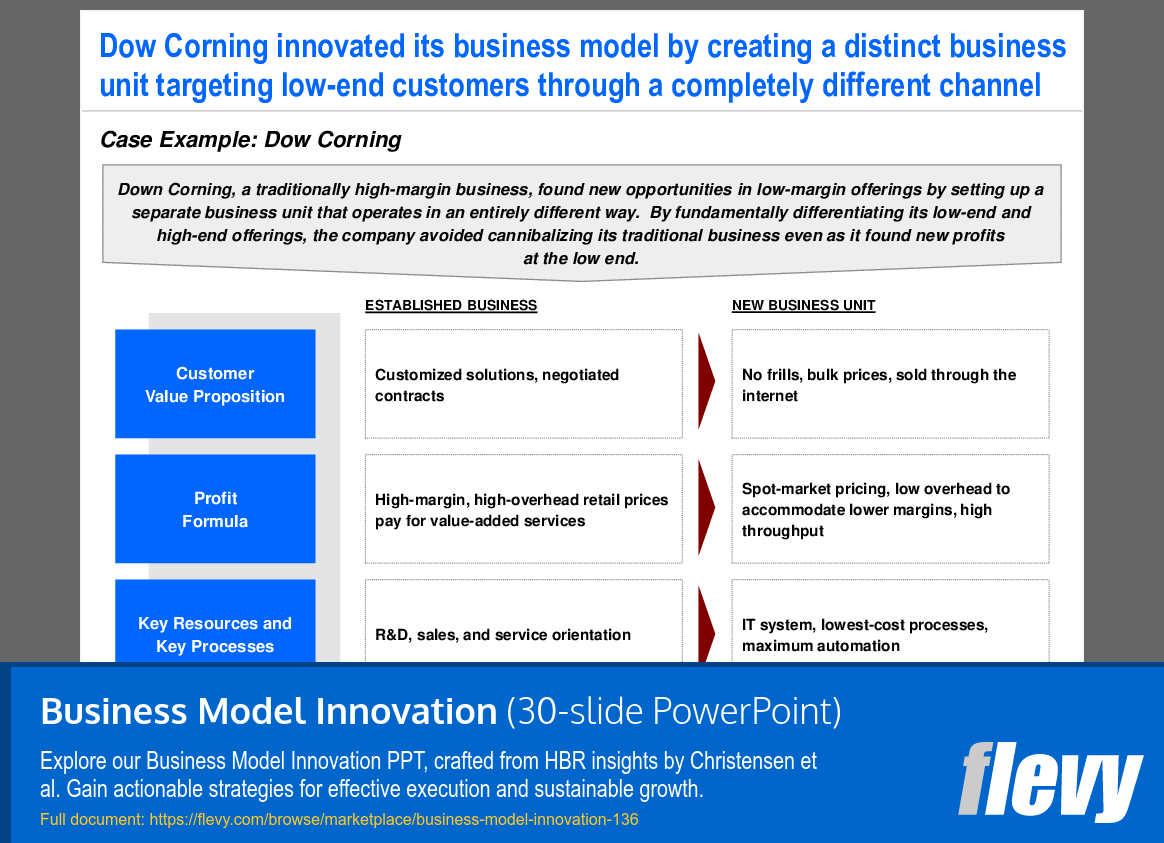
The slide outlines a case study of Dow Corning, which successfully adapted its business model to target low-end customers by establishing a separate business unit. This strategic move enabled the company to explore new market opportunities while safeguarding its traditional high-margin offerings from potential cannibalization.
On the left, the established model emphasizes a value proposition centered on customized solutions for premium clients, supported by high-margin pricing and a focus on R&D and service. In contrast, the new unit on the right adopts a simplified approach, offering bulk pricing through online sales and utilizing spot-market pricing to maintain profitability with lower margins. This shift reflects a streamlined operation that prioritizes efficiency and automation.
This analysis illustrates how Dow Corning effectively navigated market segmentation, creating a distinct unit that caters to a different customer base. Other organizations can draw valuable insights from this case to explore innovative strategies for growth while protecting existing revenue streams.
