The CEO’s Guide to Service 4.0

This article discusses slides taken from a strategy consulting presentation on Service 4.0 Transformation. You can download the full PPT here.
This presentation focuses on Service 4.0 Transformation, a pivotal shift in how service organizations deliver value in response to evolving customer expectations. It highlights the need for a more customized, proactive, and integrated service model, leveraging emerging digital technologies to enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
The core framework presented outlines a 10-dimensional approach essential for implementing Service 4.0. Each dimension, from ambition to rollout plan, is explored in detail, emphasizing the role of technologies like Big Data and RPA in facilitating this transformation. The presentation also provides practical insights and templates, making it a valuable resource for organizations aiming to thrive in the digital era.
Stages of Service Provision Evolution

The slide presents a framework for understanding the evolution of service provision, divided into 4 stages from Service 1.0 to Service 4.0. Each stage illustrates a transformation in service delivery driven by technological advancements and evolving customer expectations.
Service 1.0, originating in the 19th century, reflects a manual and non-standardized approach, exemplified by traditional bookkeeping. The transition to Service 2.0 in the early 20th century marked a shift towards standardization and industrialization, highlighted by the rise of postal services and call centers. By the late 20th century, Service 3.0 introduced automation and self-service options, leveraging personal computers and the Internet.
Currently, we are in the Service 4.0 phase, where organizations deliver proactive and customized services across integrated channels. This stage is characterized by the use of Big Data and Analytics, enabling companies to anticipate customer needs and respond in real-time, reflecting a significant advancement in service capabilities.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Identifying and Mitigating Waste in Service Industries
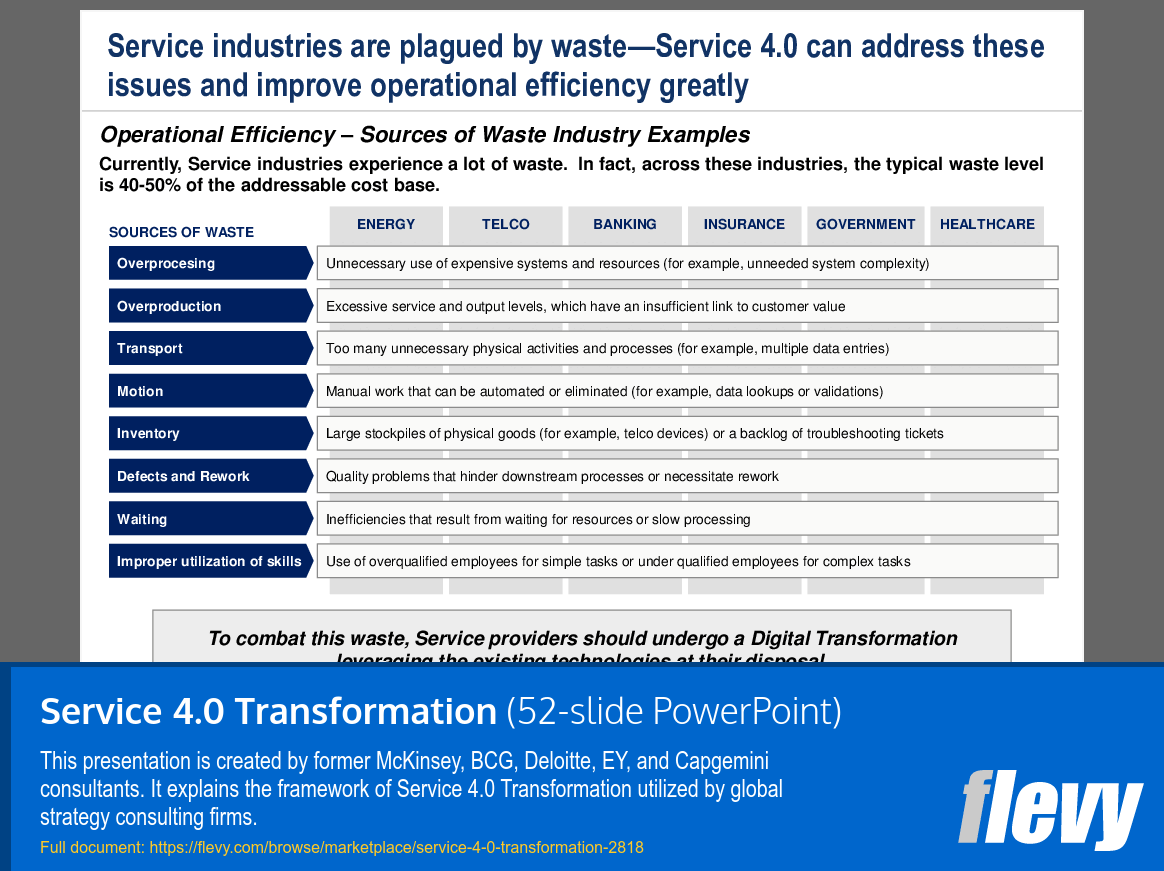
Service industries face significant waste, which leads to operational inefficiencies. The slide categorizes waste into various types, including overprocessing, overproduction, transport, motion, inventory, defects, waiting, and improper utilization of skills. Each type is illustrated with examples from sectors like energy, telecommunications, banking, and healthcare, highlighting the disconnect between service levels and customer needs.
Overprocessing involves unnecessary complexity in systems, while overproduction indicates excessive service that does not align with customer value. Transport waste complicates processes with unnecessary physical activities, and motion waste points to manual tasks that could be automated. The slide emphasizes the importance of addressing these inefficiencies through digital transformation, urging service providers to leverage existing technologies effectively.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Bridging the Gap: Customer Expectations vs. Experience

The slide highlights a significant disconnect between customer expectations and their actual experiences, which is a pressing issue in service delivery. On one side, customers anticipate simplicity, intuitiveness, and personalization, along with seamless interactions across devices. These expectations are driven by advancements in digital technology and a growing demand for high-quality service.
On the other side, the reality is starkly different. Customers encounter long wait times, inconsistencies between in-store and online experiences, and a reactive approach to service issues. This gap contributes to low customer satisfaction, indicating that many service providers are falling short of meeting evolving client needs.
Leading digital companies are addressing this gap by utilizing advanced technologies to create comprehensive customer profiles. They leverage both external and internal data to deliver personalized, real-time solutions. The emphasis on Service 4.0 illustrates the necessity for organizations to align customer expectations with actual experiences to enhance satisfaction and build long-term loyalty.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Transforming Customer Satisfaction: Service 4.0 Overview

The slide highlights a crucial shift from Service 2.0/3.0 to Service 4.0, focusing on transforming both service offerings and delivery methods to enhance customer satisfaction. Service 2.0/3.0 is characterized by a reactive, industry-specific, and standardized approach, which often lacks the flexibility needed in today’s fast-paced market. In contrast, Service 4.0 is proactive, integrated, and data-driven, allowing organizations to anticipate customer needs and provide customized solutions.
On the delivery side, Service 2.0/3.0 relies on explicit, manual interfaces and remote service centers, leading to potential delays and inefficiencies. The predefined paths in this model can restrict adaptability to unique customer situations. Service 4.0, however, utilizes implicit, virtual interfaces and seamless, omnichannel delivery, enabling real-time adjustments and a more personalized customer experience. This evolution is essential for organizations aiming to meet the changing expectations of their customers.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Framework for Service 4.0 Transformation Dimensions

The slide presents the essential elements of Service 4.0 Transformation, focusing on ten dimensions that are crucial for shaping the service provider’s operating model. These dimensions are grouped into 3 main categories: organization, people, and technology. Each dimension must be carefully evaluated to ensure a successful transformation process.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Essential Technologies Empowering Service 4.0 Innovation

The slide presents nine key technologies that drive Service 4.0 Transformation, focusing on their roles in improving efficiency throughout the value chain. Each technology is briefly outlined, showcasing its application and potential advantages for organizations. This serves as a strategic guide for decision-makers evaluating technology adoption in their Service 4.0 initiatives.
Big Data & Analytics enables organizations to understand customer behaviors better, allowing for personalized service offerings. Cloud Computing supports the management of large data volumes, facilitating on-demand service delivery. Social Media enhances customer engagement through tailored solutions based on user-generated data, while Cognitive Computing offers intelligent virtual assistance to improve interactions.
The Internet of Things (IoT) maintains ongoing connections for real-time service and remote monitoring. Smart Devices contribute to an ecosystem of applications leveraging advanced technology. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) increases operational efficiency by automating rule-based tasks. Virtualization promotes flexibility by decoupling services from specific hardware, and Augmented Reality (AR) enhances user experience by providing contextual information.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Transforming Operations with Robotic Process Automation

The slide provides a concise overview of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), defining it as a technology that employs software robots and AI to automate routine tasks typically performed by human employees. It highlights RPA’s capability to handle various rule-based functions, such as data extraction and document generation, allowing human workers to concentrate on exceptions rather than mundane tasks. This shift can lead to enhanced operational efficiency.
Three key benefits of RPA are outlined: improved employee and customer satisfaction, accelerated productivity gains, and enhanced compliance. These advantages are described as immediate and substantial, indicating that organizations can anticipate quick returns on their RPA investments. The slide also notes the rapid growth of the RPA market, projected to double every 6 months, underscoring a strong movement toward automation across sectors like finance and customer service.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Optimizing Customer Engagement through Social Media

The slide delineates the impact of social media on the Customer Experience Journey, structured into 4 key phases: Initial Consideration, Active Evaluation, Moment of Purchase, and Post-purchase Experience. Each phase outlines specific actions that brands can take to enhance customer engagement through social media platforms.
This framework illustrates how social media can be leveraged at every stage of the customer journey. By adopting a proactive approach, brands can not only meet current customer needs, but also anticipate future trends, ultimately fostering loyalty and driving growth.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Enhancing Satisfaction through Employee-RPA Collaboration

This slide outlines the benefits of integrating Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to enhance both employee and customer satisfaction. It highlights how RPA can take over repetitive tasks that employees often find tedious, allowing them to focus on more engaging and rewarding work. This shift not only boosts job satisfaction, but also fosters a sense of empowerment among employees, who begin to see robots as valuable team members.
The connection between employee happiness and customer satisfaction is emphasized, noting that RPA can lead to quicker issue resolution and improved customer service. An example workflow illustrates how RPA streamlines operations, showcasing the efficiency gains from automating data processing and system updates. A cautionary note is included about the future of AI and its potential to take over tasks traditionally performed by humans, raising important questions about workforce roles moving forward.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Structured Six-Phase RPA Deployment Framework

This slide presents a six-phase framework for implementing a Robotic Process Automation (RPA) solution. The process starts with defining the RPA perimeter, where organizations assess which processes are suitable for automation and their readiness for RPA. Key considerations include identifying potential efficiency gains and ensuring processes are primed for automation.
The next phases involve optimizing existing processes to eliminate inefficiencies, choosing the right RPA solution — either in-house development or purchasing a market option — and defining the optimal relationship between human workers and RPA. Finally, organizations must study the impacts on their operating model and build a comprehensive deployment plan that includes programming, integration, and risk management strategies.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Integrating Smart Devices for Enhanced Customer Engagement

The slide addresses the integration of smart devices into a unified customer engagement strategy. It highlights the growing number of platforms and applications, stressing the need for a cohesive Customer Journey Strategy that connects all customer touchpoints. This integration is vital for ensuring a seamless experience as customers transition between different platforms and devices.
A smooth customer experience is emphasized, particularly in scenarios where customers switch from one support channel to another without having to repeat their issues. The slide also notes the importance of collecting data from various smart devices, which should be centralized for effective analysis. This data-driven approach enables companies to tailor their engagement strategies based on customer behavior.
An example from T-Mobile illustrates this concept through its mobile app, T-Mobile Tuesdays, which offers exclusive deals to subscribers. This initiative not only enhances customer engagement, but also demonstrates how smart devices can be leveraged to improve customer satisfaction. The overall message underscores the necessity of an integrated approach to customer interactions across smart devices.
