The COO’s Guide to Cost Reduction Methodologies
This article discusses slides taken from a management consulting presentation on Cost Reduction Methodologies. You can download the full PPT here.
This presentation focuses on common cost reduction methodologies, a critical area for organizations aiming to enhance operational efficiency and drive profitability. It covers 4 core strategies such as Process Optimization, Strategic Sourcing, Shared Services, and Business Process Outsourcing, providing a comprehensive overview of how to identify and prioritize savings opportunities.
At the heart of the presentation is the Savings Prioritization Matrix, a tool designed to help executives pinpoint high-impact cost reduction areas. It aligns initiatives with strategic business goals, ensuring that efforts are both effective and sustainable.
Additionally, the document outlines a structured Activity Based Assessment approach, breaking down the process into 4 essential steps, which guide organizations from diagnostics to actionable transformation plans.
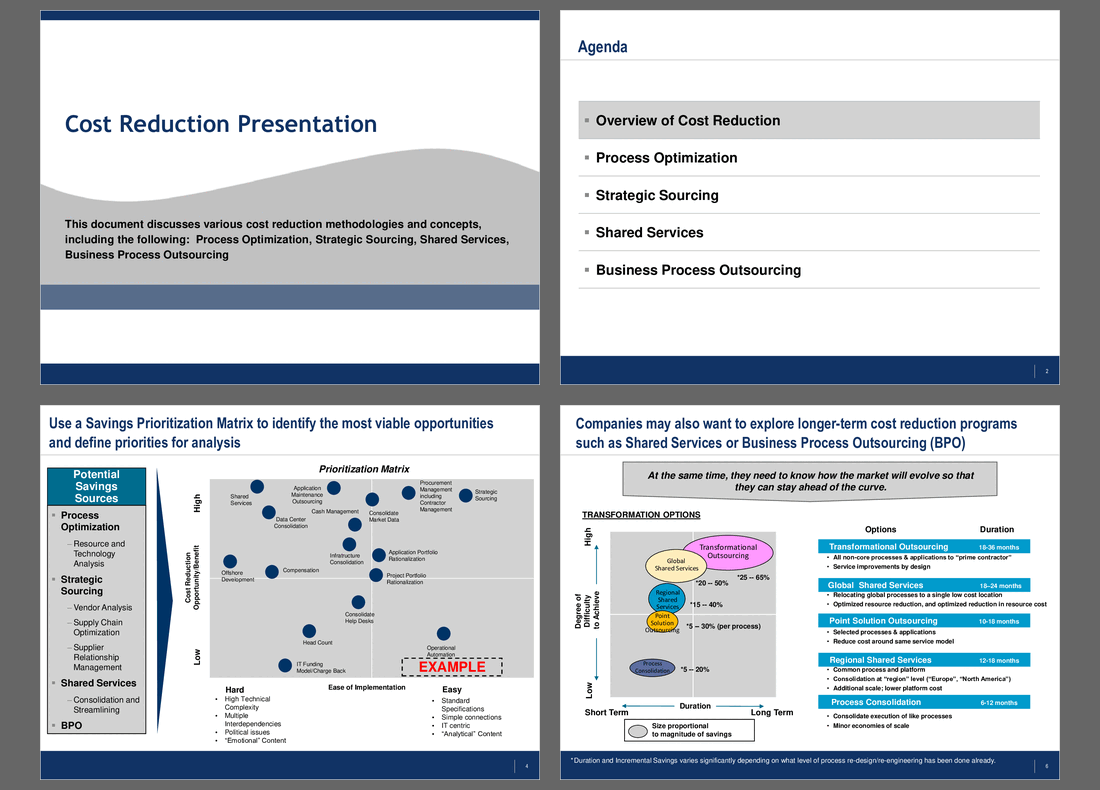
Prioritization Matrix for Cost Reduction Opportunities
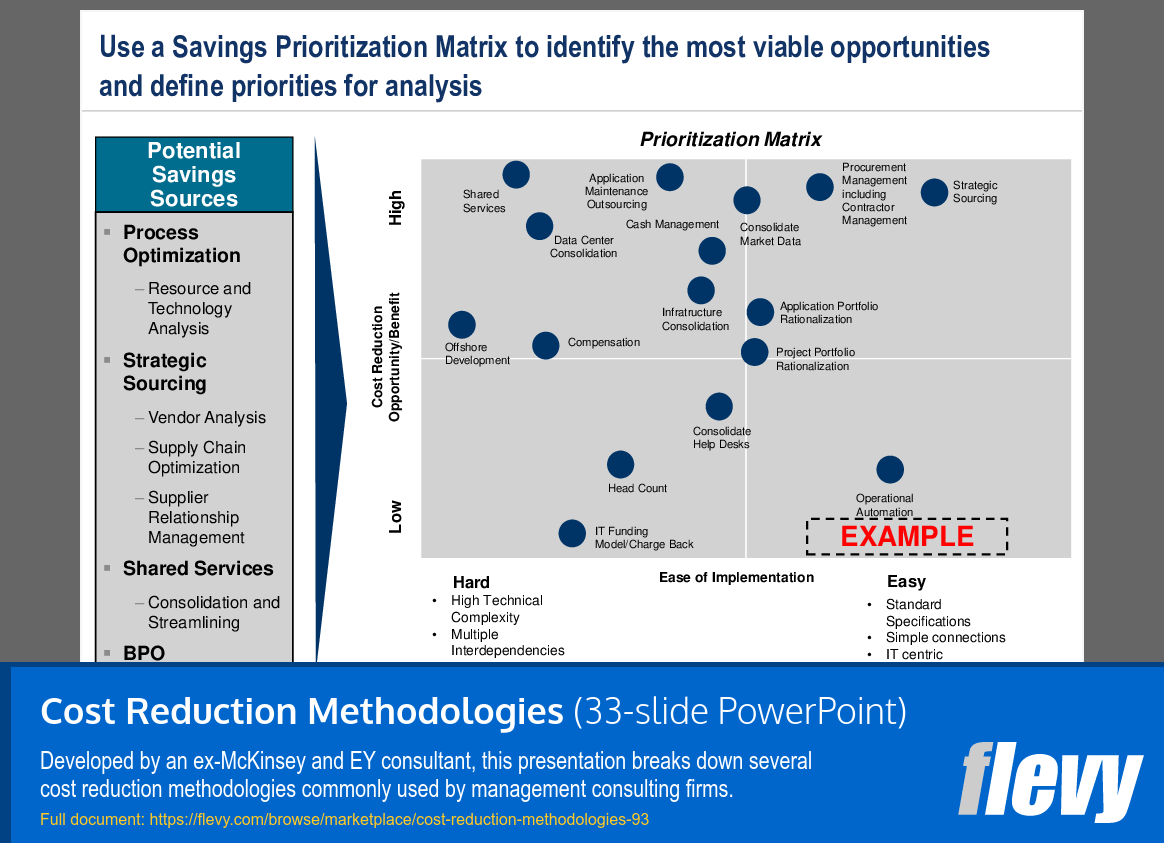
The Savings Prioritization Matrix is a tool designed to help organizations pinpoint and rank cost reduction opportunities. It uses a two-dimensional framework where the vertical axis represents the potential financial impact of savings, while the horizontal axis indicates the ease of implementation. This setup allows executives to quickly visualize which initiatives could deliver significant returns with minimal complexity.
This visual representation supports informed decision-making by balancing potential savings against implementation challenges. It ensures that resources are allocated efficiently, focusing on initiatives that promise the best outcomes with the least resistance.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Cost Reduction Strategies: Transformation Options Overview
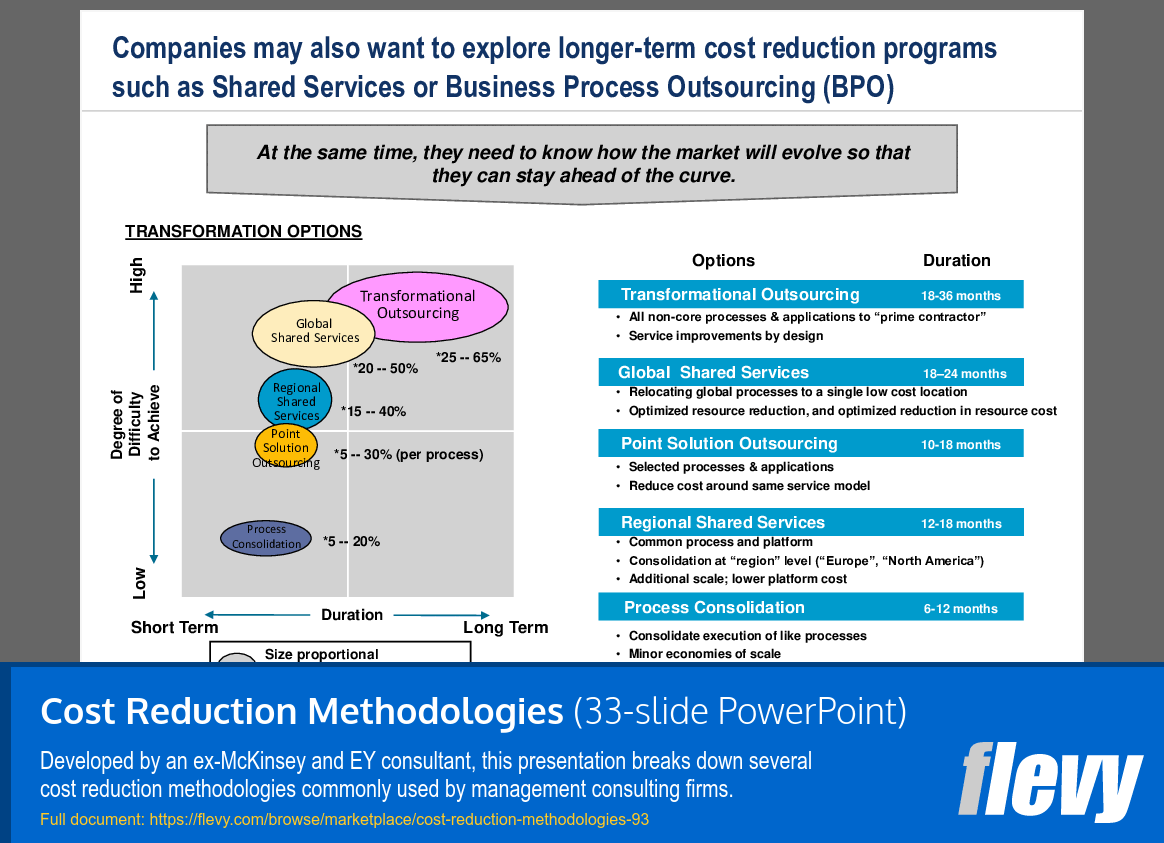
The slide presents various transformation options for companies aiming to implement long-term cost reduction strategies through Shared Services and Business Process Outsourcing (BPO). It categorizes these options based on the difficulty of implementation and the duration required, highlighting “Transformational Outsourcing” as the most comprehensive choice. This approach entails outsourcing all non-core processes to a prime contractor, with a significant potential for cost reduction ranging from 25% to 65% over an 18 to 36-month period.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Identifying Cost-Value Misalignments through Focus Interviews
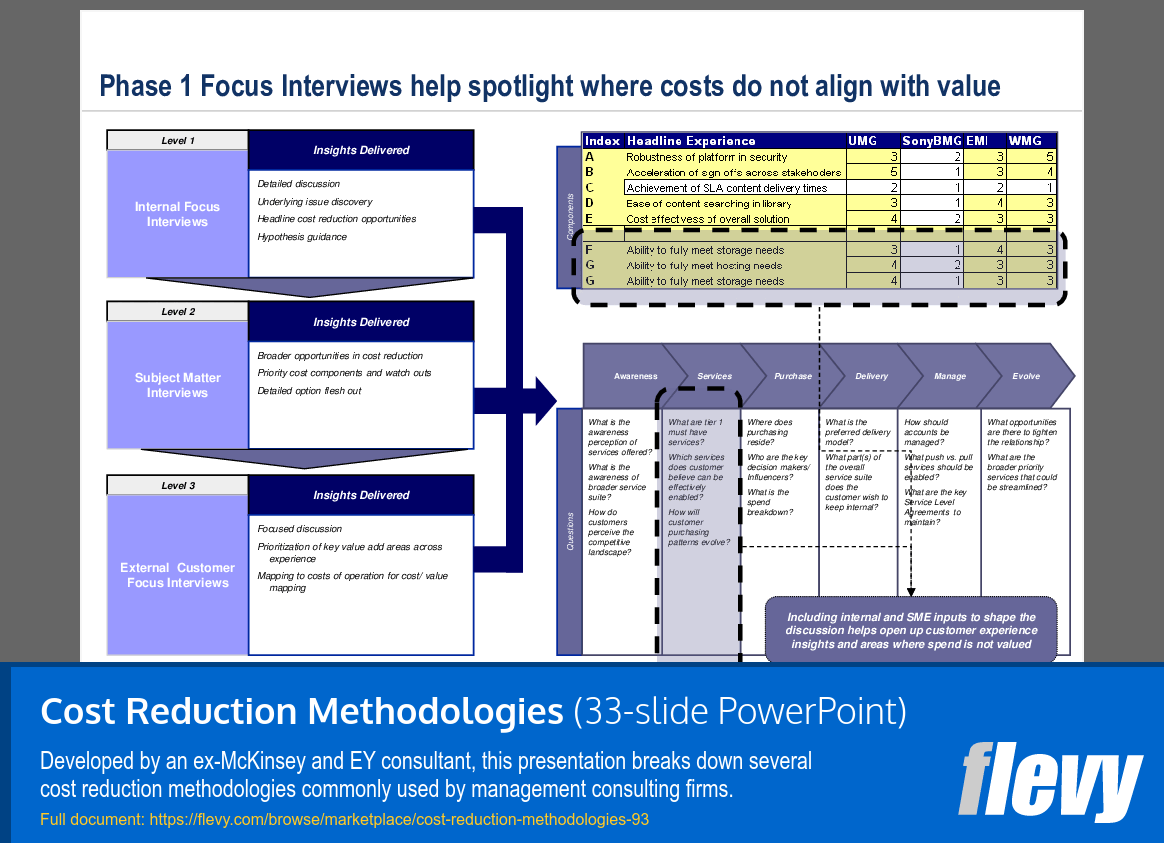
The slide presents a structured method for identifying misalignments between costs and value through focus interviews. It categorizes these interviews into 3 levels: Internal Focus, Subject Matter, and External Customer Focus. Each level aims to deliver targeted insights that can inform strategies for cost reduction.
Internal Focus Interviews delve into underlying issues and potential cost-saving opportunities, emphasizing a proactive approach. Subject Matter Interviews broaden the scope, prioritizing key cost components while highlighting potential risks. External Customer Focus Interviews shift the focus to customer perceptions, mapping operational costs against the value customers expect.
An index evaluates various experiences across organizations, offering a comparative analysis in areas like security and content management. This benchmarking serves as a vital tool for organizations to assess their performance and identify gaps, ultimately guiding informed decision-making in cost management strategies.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Order to Cash Performance Benchmark Analysis
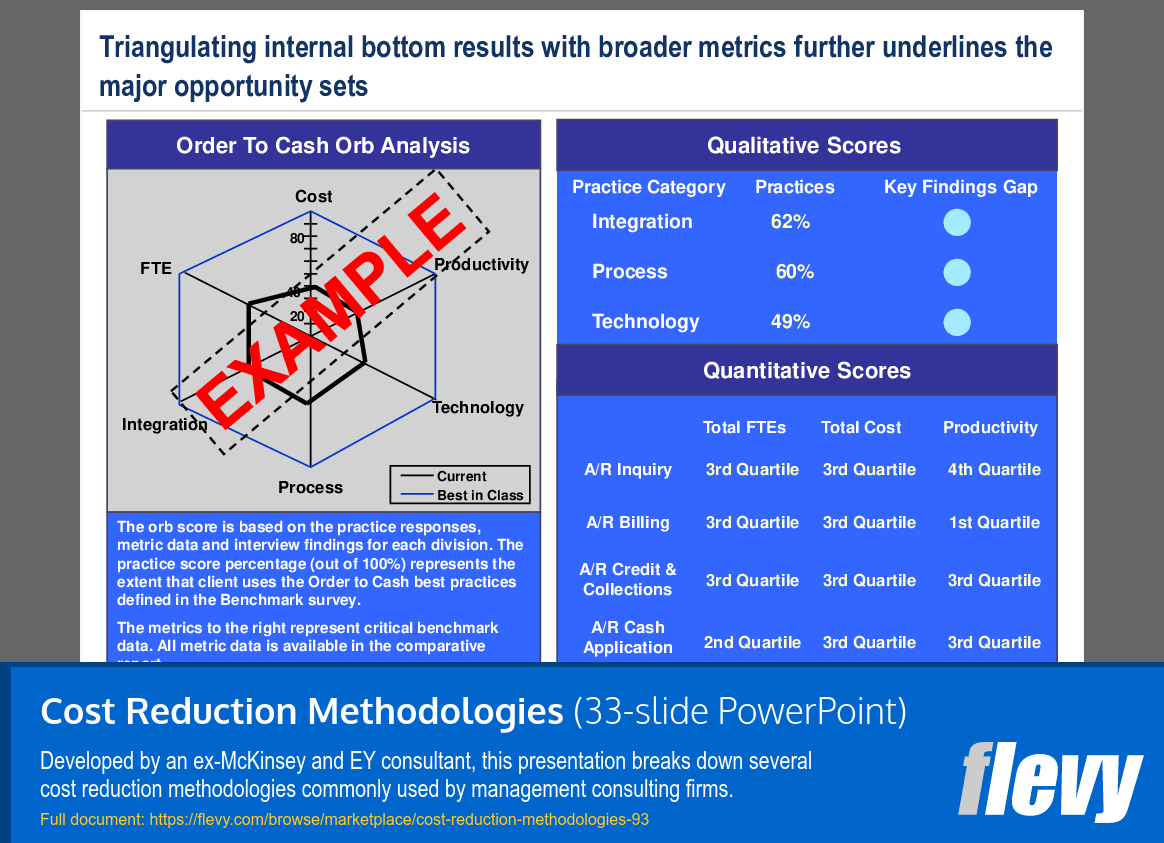
The slide provides a detailed analysis of the Order to Cash (O2C) process using a three-dimensional orb model. It compares current performance against industry benchmarks across key metrics: Cost, Productivity, and Technology, while also considering Integration and Process dimensions. This visualization helps pinpoint the organization’s standing relative to best practices in the sector.
Qualitative scores reveal varying maturity levels, with Integration at 62%, Process at 60%, and Technology significantly lower at 49%. This indicates a solid understanding of Integration and Process,, but highlights a critical need for improvement in Technology. The quantitative metrics further break down performance in accounts receivable functions, showing most fall within the third quartile, except for A/R Cash Application, which performs slightly better.
The analysis underscores the necessity of aligning internal results with broader industry metrics to identify gaps and prioritize improvement initiatives. This approach serves as a vital tool for executives aiming to enhance their O2C processes and drive operational efficiency.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Structured Four-Phase Sourcing Methodology Overview
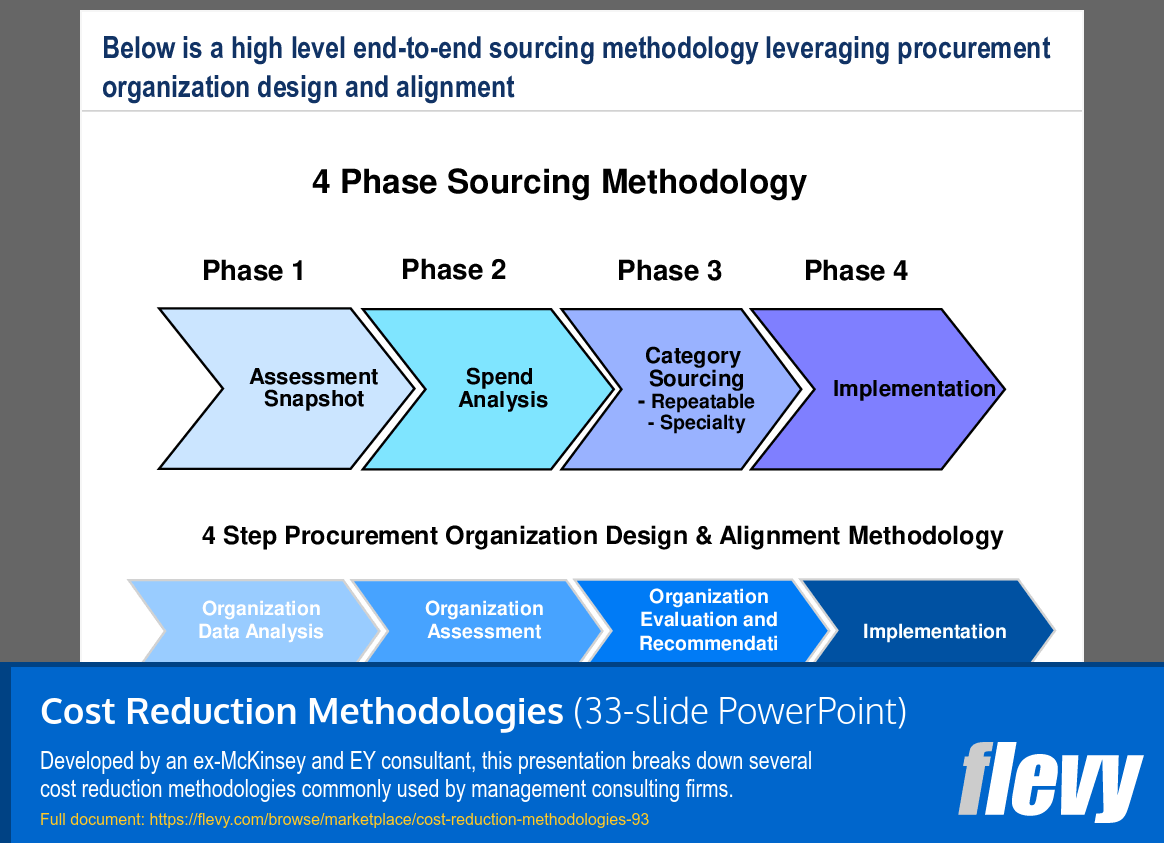
The slide presents a structured four-phase sourcing methodology aimed at improving procurement organization and alignment. Each phase plays a vital role in guiding organizations through the sourcing process, ensuring a thorough approach to procurement practices.
Phase 1, “Assessment Snapshot,” involves evaluating current procurement capabilities to identify improvement areas. Phase 2, “Spend Analysis,” focuses on analyzing spending patterns to uncover cost-saving opportunities. The third phase, “Category Sourcing,” categorizes procurement needs into repeatable and specialty sourcing, enhancing supplier relationships and negotiation outcomes.
Finally, Phase 4, “Implementation,” translates strategies into actionable results, aligning procurement practices with business objectives. The slide also includes a secondary framework for organizational design, which supports the sourcing methodology through data analysis and evaluation, ensuring effective procurement practices are in place.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Organizational Framework for Shared Services Centers
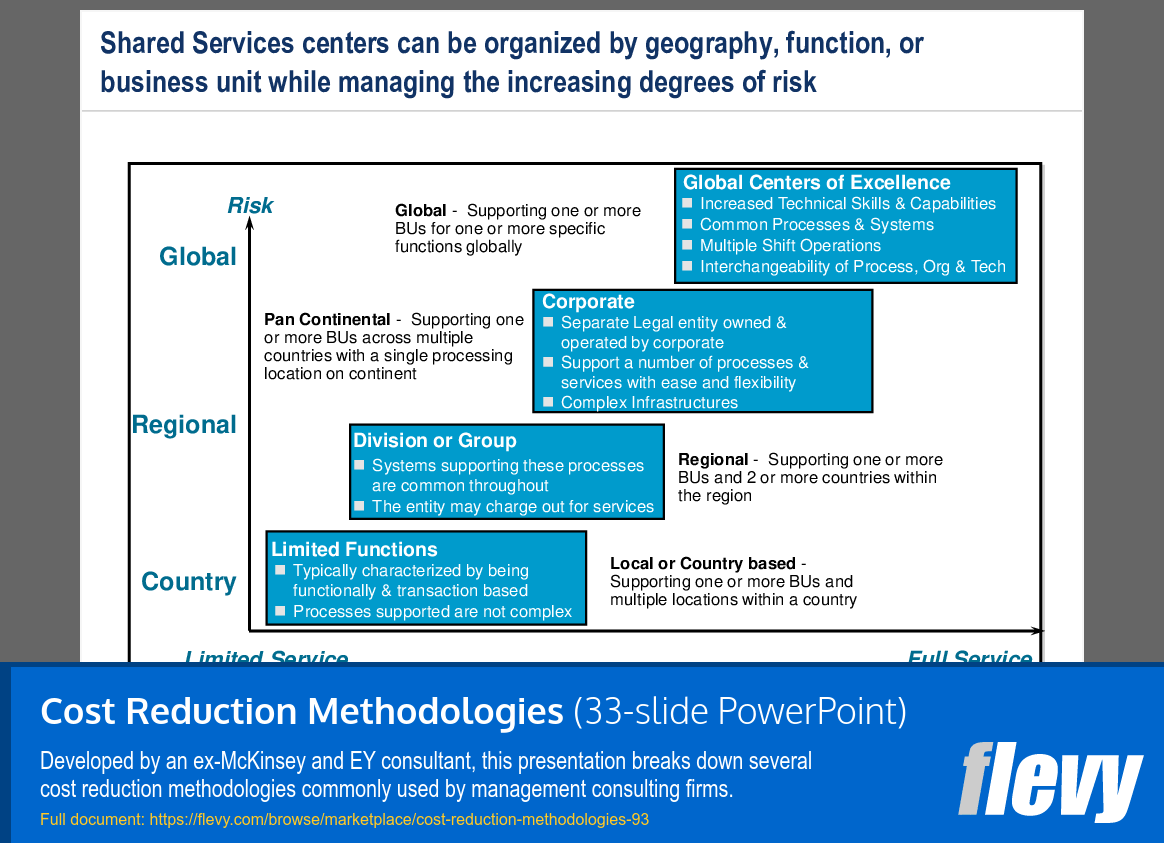
The slide presents a framework for organizing Shared Services centers, categorized by Global, Regional, Country, and Limited Functions. Each category has unique characteristics and operational scopes, addressing varying levels of risk. The Global category supports multiple business units across various functions worldwide, with a Pan Continental model enhancing efficiency by centralizing operations across countries.
The Regional category allows for localized support across multiple countries while maintaining centralized control. Corporate centers can operate as separate legal entities, offering a range of services with complex infrastructures. The Division or Group section emphasizes the need for common systems, facilitating service chargebacks, while Limited Functions focus on straightforward operations, typically handling specific transactions.
This framework serves as a strategic guide for organizations looking to establish or restructure Shared Services centers. It provides insights into aligning configurations with business needs and managing risk effectively, aiding in resource allocation and operational efficiency decisions.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Comprehensive Framework for Shared Services Implementation
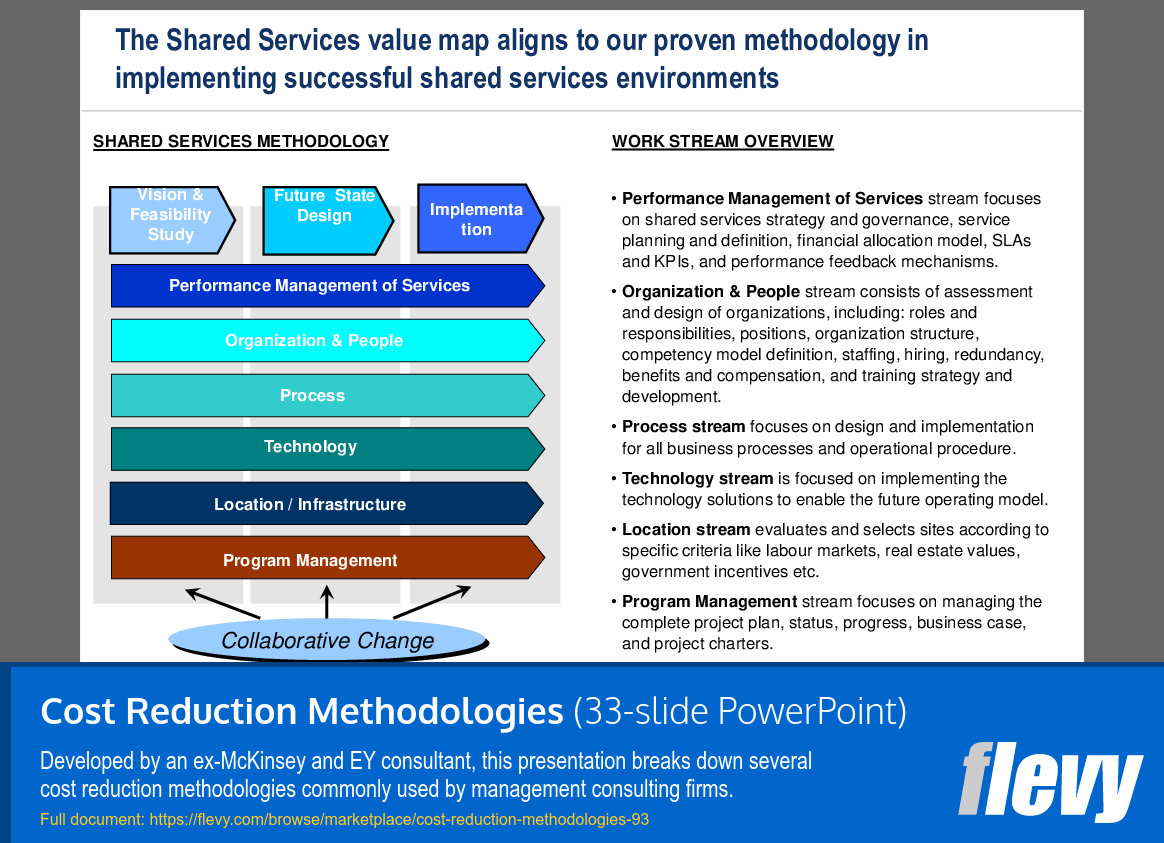
The slide outlines a structured methodology for implementing shared services, detailing key phases such as Vision & Feasibility Study, Future State Design, and Implementation. Each phase is crafted to facilitate a smooth transition to a shared services model, ensuring that organizations can effectively adapt to this operational framework.
Performance Management of Services is emphasized as a core element, focusing on governance and strategic alignment through service level agreements and key performance indicators. The Organization & People stream addresses the necessary human resources, ensuring roles and responsibilities are clearly defined to support the shared services framework. Additionally, the Process and Technology streams are critical for designing efficient procedures and deploying the right technological solutions.
Program Management is highlighted as essential for overseeing the project lifecycle, including planning and status tracking. The Collaborative Change aspect underscores the importance of engagement across all organizational levels for successful implementation. This multifaceted approach is crucial for organizations aiming to optimize their shared services environments.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Framework for Optimizing Business Activity Management
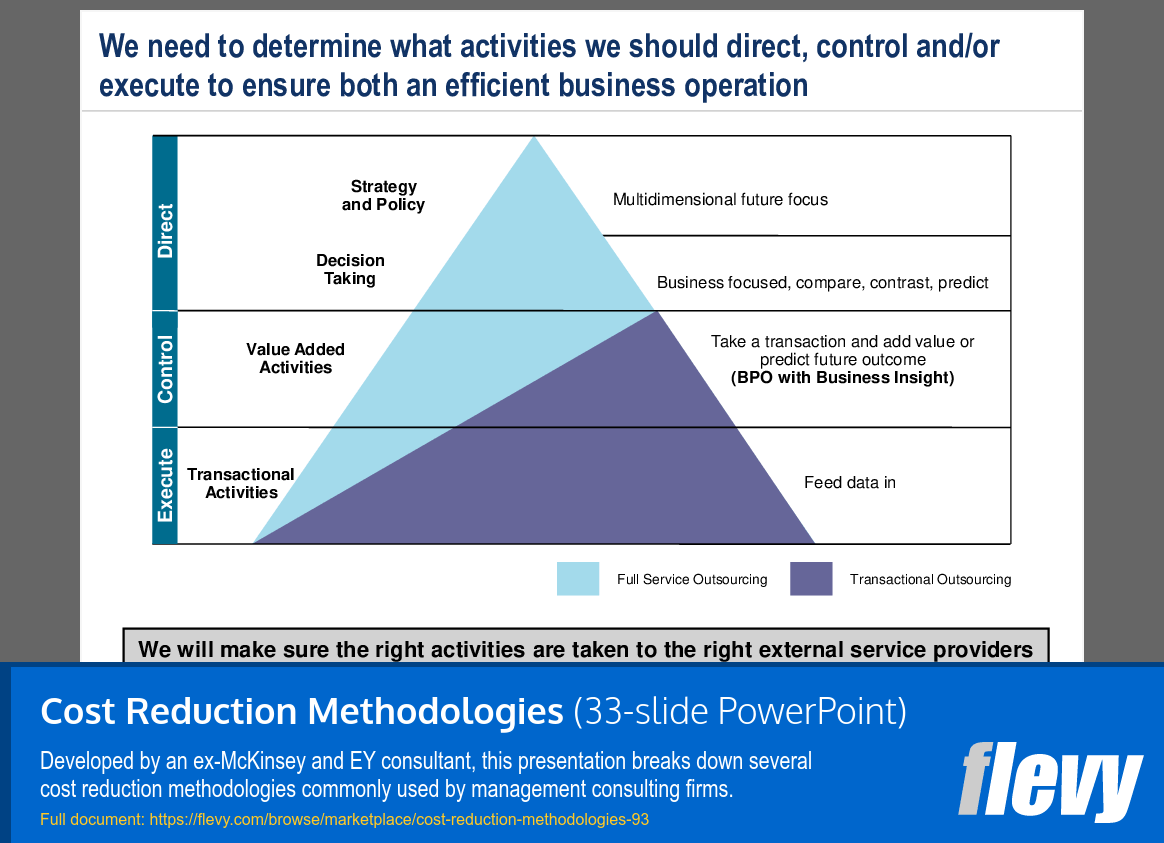
The slide presents a framework for optimizing business activities to enhance operational efficiency, structured as a triangular model with 3 categories: Direct, Control, and Execute. At the apex, “Direct” encompasses high-level strategic elements like “Strategy and Policy” and “Decision Taking,” emphasizing the importance of multidimensional thinking in leadership decisions.
