The Executive’s Guide to Performance Management Maturity Model

This article discusses slides taken from a strategy consulting presentation on the Performance Management Maturity Model. You can download the full PPT here.
The presentation centers on the concept of Performance Management Maturity, a critical topic for organizations striving for enhanced operational effectiveness. It emphasizes the importance of developing people, processes, technology, and capabilities to achieve higher performance levels.
At its core, the presentation introduces a five-level maturity model that assesses an organization’s performance management capabilities. Each level — Initial, Emergent, Structured, Integrated, and Optimized — provides a framework for evaluating current practices and identifying necessary steps for advancement. The model is supported by detailed assessment criteria and practical tools, ensuring a structured approach to achieving high performance.
Core Elements for Performance Management Maturity

The slide outlines a framework for evaluating maturity in Performance Management through 5 operational levers: Tools, Processes, Governance, Architecture, and Integration. Each lever is essential for organizations aiming to enhance their performance management capabilities. Developing strengths in these areas is crucial for achieving a higher maturity level.
Tools encompass the technologies and software that aid in performance measurement and analysis. Processes refer to the methodologies that ensure consistent management practices. Governance involves the structures that guide decision-making, while Architecture focuses on the systems that support performance initiatives. Integration ties these elements together, ensuring they function cohesively rather than in isolation.
Understanding and assessing these levers allows organizations to pinpoint areas needing improvement. This assessment can lead to better alignment with strategic objectives and enhanced operational efficiency, ultimately driving performance outcomes.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Initial Stage Overview of Performance Management Maturity

Organizations at the initial stage of the Performance Management Maturity Model lack essential tools and understanding for effective performance management. They focus primarily on immediate outcomes, neglecting long-term strategic goals. This stage is characterized by inconsistent and unconnected processes, with overlapping activities due to a lack of a structured approach.
The governance structure is simplistic and vertical, lacking clear roles and accountability. There is no explicit strategy, and informal control systems prevail. Initial implementation efforts are underway,, but they lack depth, and integration of performance management practices is minimal, with little knowledge and limited software usage.
Overall, these organizations do not engage in practices that promote employee development or innovation. This analysis highlights critical areas for improvement, serving as a valuable insight for potential customers assessing their current performance management practices.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Initial Stage of Performance Management Maturity Insights
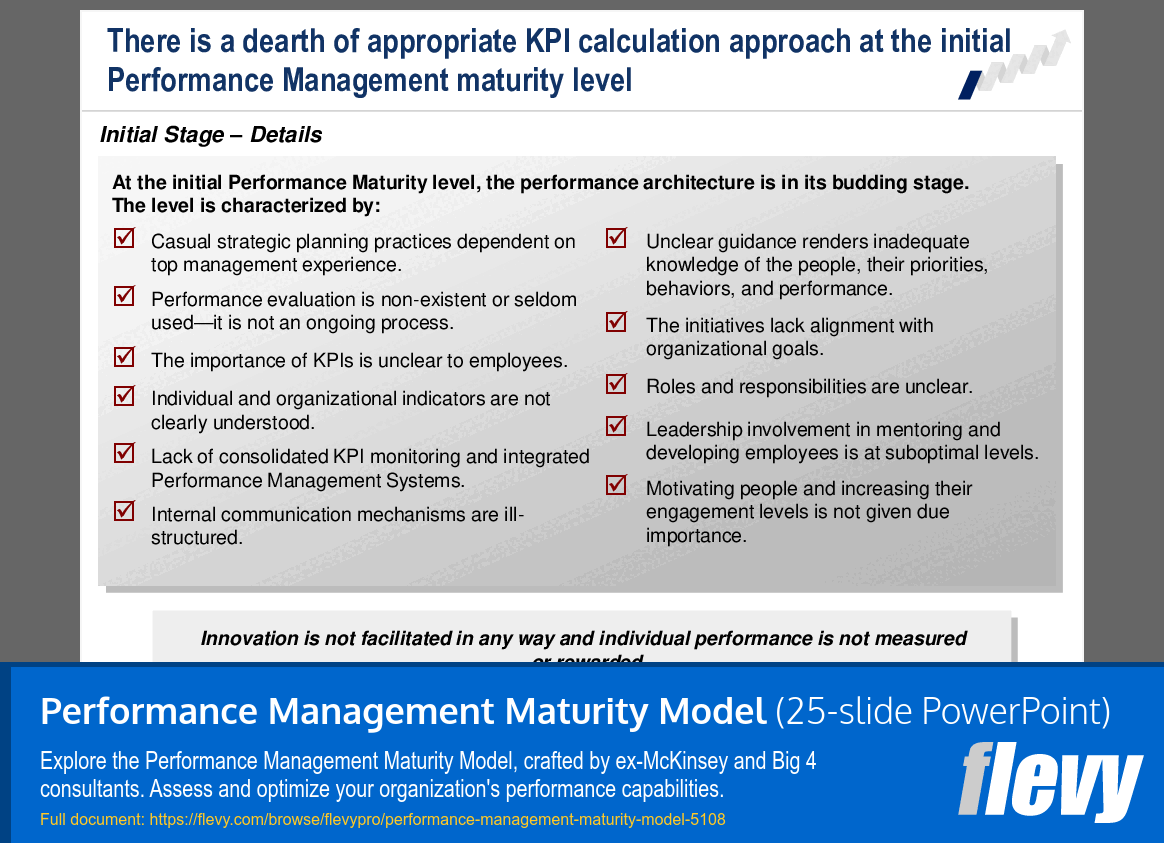
The slide details the initial stage of the Performance Management Maturity Model, highlighting significant deficiencies in performance management practices. Strategic planning is often informal, relying heavily on top management’s experience, which leads to inconsistent results. Performance evaluations are rarely conducted, resulting in a lack of ongoing assessment and feedback mechanisms.
Employees face challenges in understanding Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) due to unclear definitions and communication. This confusion extends to both individual and organizational performance metrics, creating a fragmented approach. Additionally, poorly structured internal communication and minimal leadership involvement in employee development hinder growth and engagement.
Overall, the content underscores foundational issues that organizations must address to advance in maturity. A structured approach to performance management, with clear communication and active leadership engagement, is essential for aligning with strategic objectives and fostering a motivated workforce.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Structured Approach to Key Performance Indicators

The “Structured” Performance Maturity level emphasizes a systematic method for selecting Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). KPIs are chosen based on clear criteria and established tools, ensuring organizational consensus. This approach aligns performance metrics with strategic objectives, making it essential for effective performance management.
Documentation of KPIs is standardized, enhancing consistency across the organization. Targets are set using benchmarking and market comparisons, ensuring relevance and achievability. A well-defined Performance Management System supports this process, providing templates and guidelines that facilitate accurate tracking and reporting.
Employees understand both organizational and individual performance goals, fostering a culture that values performance management. Individual appraisals are linked to personal KPIs, promoting accountability. The inclusion of incentives and training opportunities reflects a commitment to employee development, ultimately creating a cohesive performance culture that optimizes organizational capabilities.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Characteristics of High-Performing Organizations in Maturity Model

The slide details the characteristics of organizations at the “Optimized Stage” of performance management systems. These organizations have implemented advanced processes for selecting Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that align with both strategic objectives and individual roles. A centralized KPI library ensures accurate calculation and reporting, fostering consistency across the board.
Automation is integral, utilizing scorecards and Business Intelligence tools to visualize data effectively. Employees have clearly defined roles, which enhances accountability and authority. The culture in these organizations promotes empowerment and motivation, driving innovation and engagement through gamification strategies that develop staff capabilities.
Recognition and rewards for achieving various tiers of objectives reinforce a culture of continuous improvement. This approach not only focuses on metrics, but also cultivates an environment that encourages learning and process enhancement, ultimately leading to high performance.
