The Executive’s Guide to Post-merger Integration (PMI)
This article discusses slides taken from a strategy consulting training presentation on Post-merger Integration. You can download the full PPT here.
This presentation focuses on Post-merger Integration (PMI), a critical management topic that addresses the complexities organizations face when merging. It emphasizes the importance of a well-structured approach to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the value derived from the merger.
The core framework outlined in the training material consists of a comprehensive methodology that spans Day One readiness, synergy capture, and functional integration across key areas such as IT, finance, supply chain, and HR.
It also provides actionable insights and detailed plans, including a 30-day action list and templates for data collection, aimed at facilitating effective integration and aligning resources to mitigate risks and achieve strategic objectives.
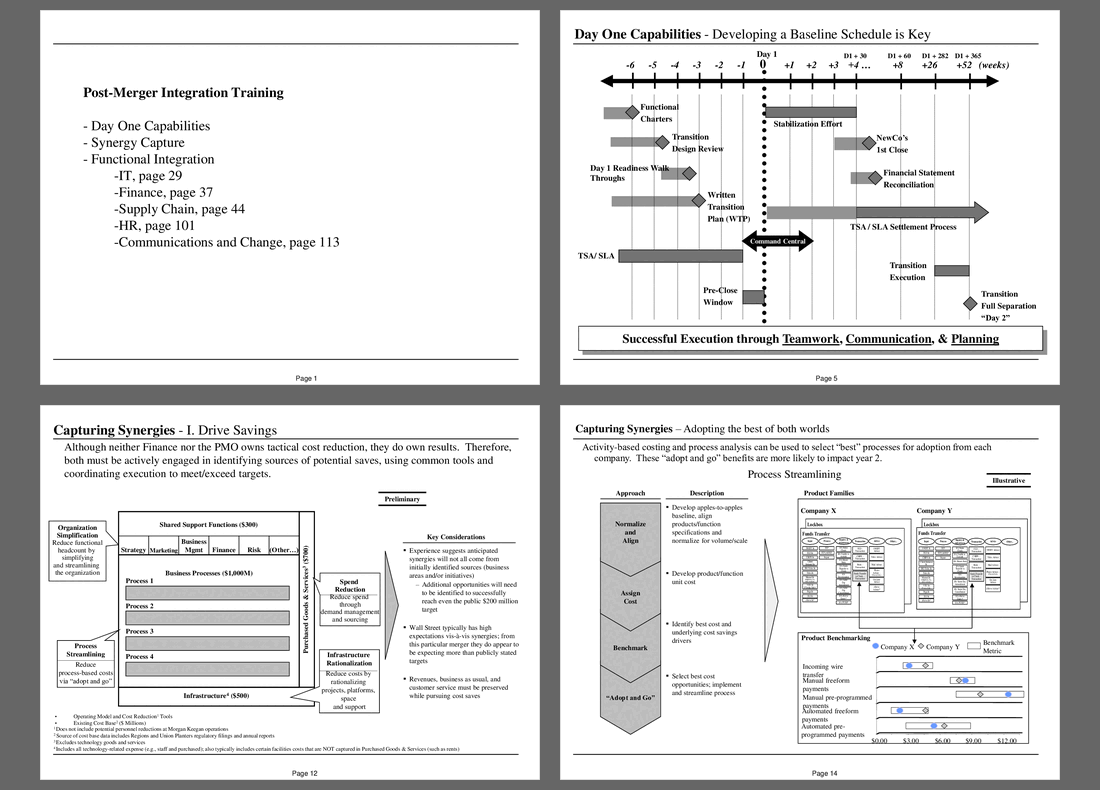
Day One Integration Timeline and Key Activities
The slide presents a timeline for Day One capabilities essential for PMI, spanning from 6 weeks prior to Day One to one year afterward. It highlights the necessity of a baseline schedule to ensure a seamless transition, marking critical milestones and activities that must be managed effectively. Key components include the establishment of functional charters, readiness walk-throughs, and the Transition Design Review, which are vital for team alignment and preparedness.
As the timeline unfolds, it captures significant actions such as the stabilization effort, the first close of the new entity, and financial statement reconciliation. The Transition Services Agreement and Service Level Agreement settlement processes are also noted, underscoring their role in defining operational frameworks during the transition. The Command Central section emphasizes the need for centralized oversight to coordinate these activities, reinforcing the ongoing nature of integration beyond initial efforts.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
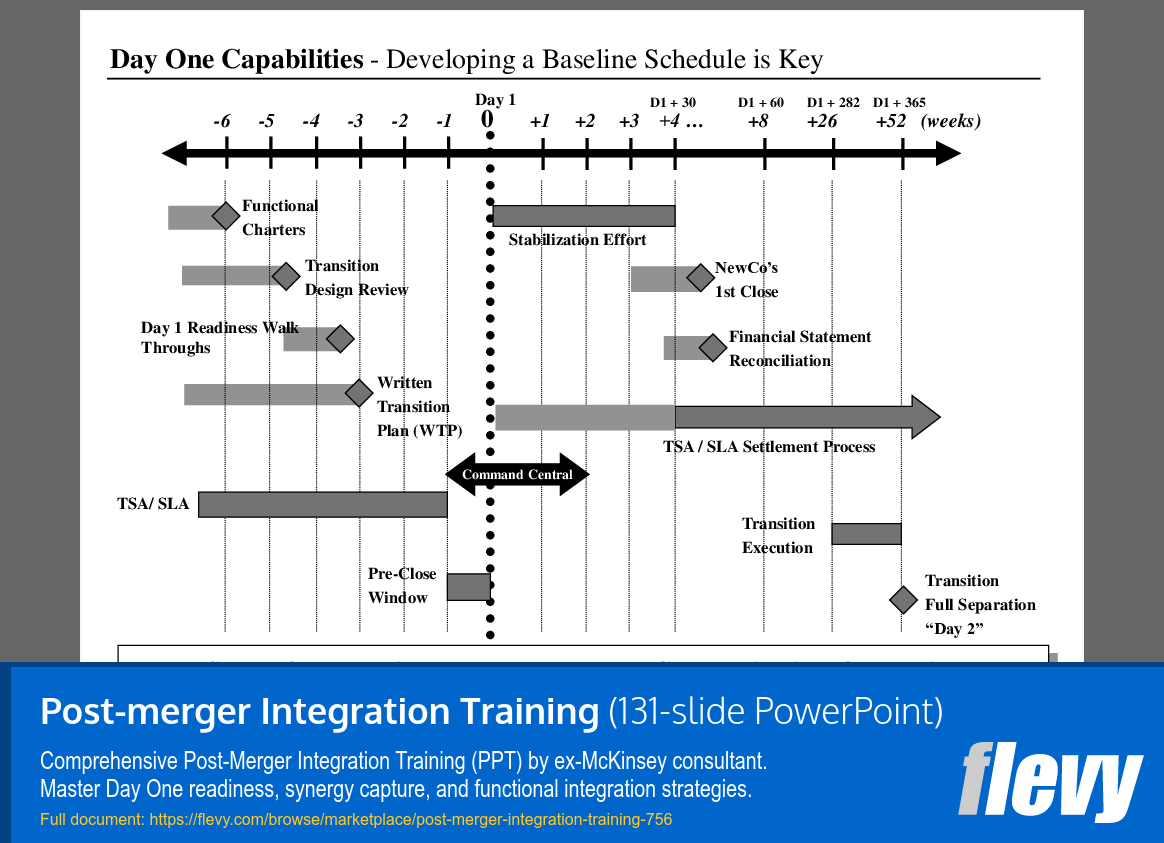
Strategic Framework for Post-Merger Cost Savings
The slide titled “Capturing Synergies — I. Drive Savings” presents a framework for achieving cost savings in a post-merger environment. It highlights the essential roles of Finance and the Project Management Office (PMO) in identifying savings opportunities, even though they do not directly manage cost reductions. Their collaboration is vital for effective execution and meeting targets.
Key components include a focus on “Shared Support Functions,” which aims to streamline operations and reduce functional headcount across various business areas. The slide also identifies 4 major business processes valued at $1 billion that should be scrutinized for efficiency improvements. Strategies like spend reduction and infrastructure rationalization are detailed, emphasizing the need to manage demand and optimize resources.
It’s crucial to recognize that anticipated savings may not solely come from initially identified areas. Additional opportunities must be explored to meet or surpass the publicly stated $200 million target. Stakeholders expect more than what has been communicated, and maintaining revenue and customer service during this process is essential for long-term success.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Optimizing Processes Post-Merger: A Strategic Framework

The slide titled “Capturing Synergies — Adopting the best of both worlds” outlines a methodical approach to streamlining processes during post-merger integration. It highlights the role of activity-based costing and process analysis in identifying effective practices from the merging companies. The slide is organized into 2 sections: “Approach” and “Product Benchmarking,” providing a clear framework for executives to follow.
The “Approach” section details 4 strategies: Normalize and Align, Assign Cost, Benchmark, and “Adopt and Go.” Each strategy focuses on creating a consistent baseline, determining unit costs, identifying cost-saving measures, and anticipating benefits in the second year post-merger. The “Product Benchmarking” section visually compares product families from both companies, showcasing various payment methods and benchmark metrics to pinpoint best practices and areas for improvement.
This slide serves as a practical guide for decision-makers aiming to leverage existing processes to enhance operational efficiency and effectiveness in a post-merger context. Its structured insights offer valuable direction for maximizing value creation during integration.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Strategies for Optimizing Tax-Related Savings
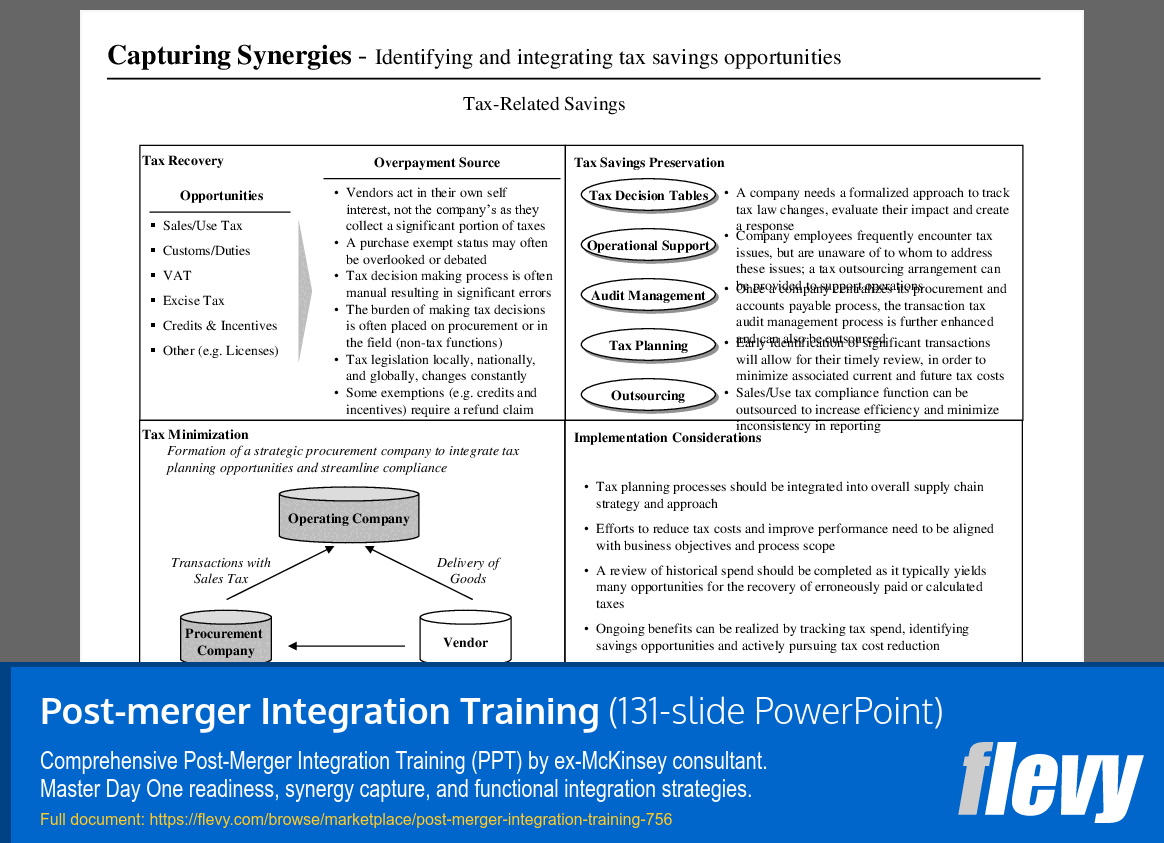
The slide titled “Capturing Synergies — Identifying and integrating tax savings opportunities” outlines strategies for enhancing tax efficiency through 2 main sections: Tax Recovery and Tax Minimization. The Tax Recovery section identifies key areas such as Sales/Use Tax, Customs/Duties, and VAT, emphasizing the need for a structured approach to manage tax decisions. It points out that vendors may overlook tax statuses, leading to manual errors and missed opportunities, particularly as tax legislation evolves.
The Tax Savings Preservation segment stresses the importance of formalizing tax decision processes within companies. Employees often face tax issues without clear guidance on resolution. Outsourcing certain tax functions can improve efficiency and reduce reporting inconsistencies. The slide also highlights the necessity of integrating tax planning into the overall supply chain strategy, recommending a review of historical spending to uncover potential tax recovery opportunities for long-term financial health.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Framework for Cost Reduction in Post-Merger Integration
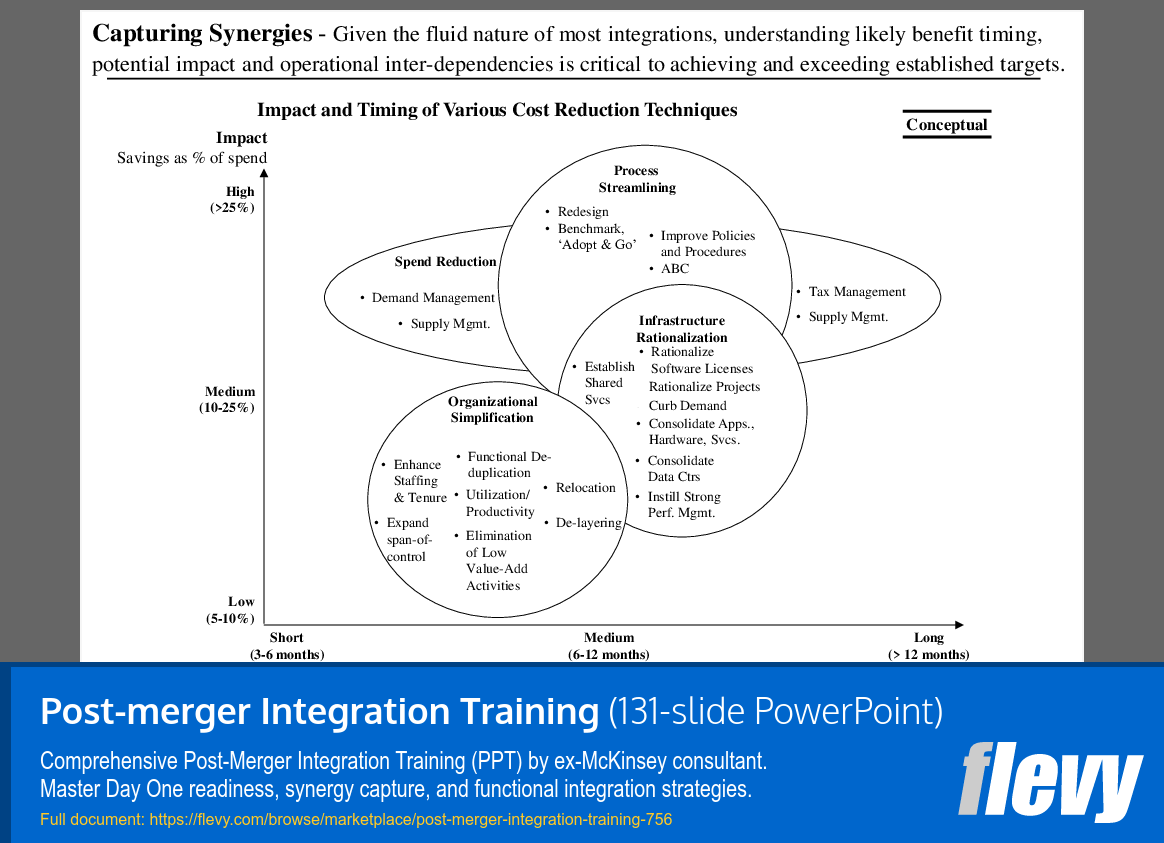
The slide titled “Capturing Synergies” outlines a framework for cost reduction techniques relevant to post-merger integration. It categorizes these techniques by their potential impact on savings and the timing of their implementation, which is vital for enhancing efficiency during this transition. The vertical axis measures impact, ranging from low savings of 5–10% to high savings exceeding 25%, while the horizontal axis indicates the timing from short-term (3–6 months) to long-term (>12 months).
Understanding this framework is crucial for executives navigating the complexities of PMI. It provides a clear roadmap for prioritizing initiatives that can deliver significant savings while considering their timing. This insight is instrumental in meeting and exceeding financial targets during critical transition periods.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Comprehensive IT Integration Framework for M&A
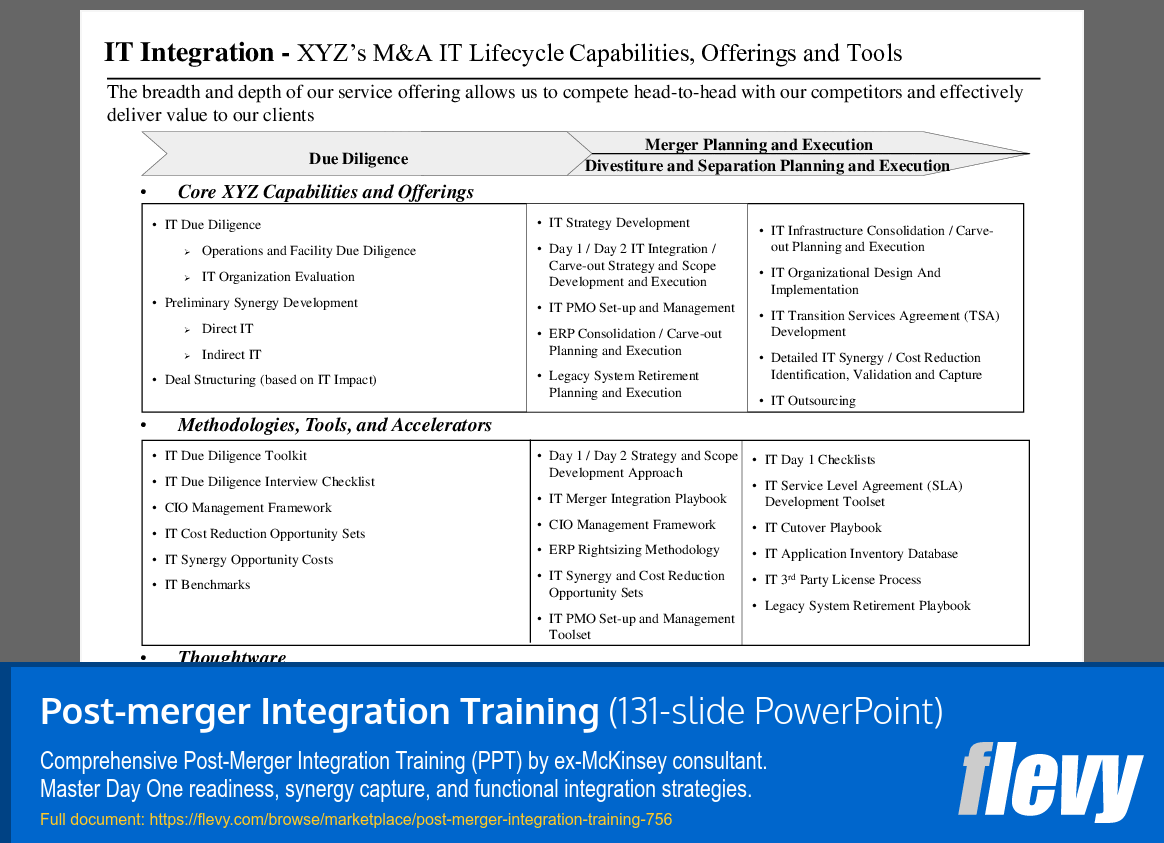
The slide presents XYZ’s extensive capabilities in IT integration across the M&A lifecycle, focusing on 3 main phases: Due Diligence, Merger Planning and Execution, and Divestiture and Separation Planning. Each phase outlines specific services, methodologies, and tools designed to create substantial value for clients. The emphasis is on a structured approach that enhances efficiency and reduces costs.
In the Due Diligence phase, core offerings include IT assessments and preliminary synergy development, which highlight both direct and indirect IT impacts. The Merger Planning and Execution section stresses the importance of IT strategy development and project management, ensuring a seamless transition during mergers. For Divestiture and Separation Planning, capabilities like infrastructure consolidation and transition services agreements are crucial for effective management and value maximization.
The methodologies and tools section lists resources such as due diligence toolkits and management frameworks. These support the execution of strategies throughout the M&A process. Overall, the slide illustrates XYZ’s readiness to assist clients in navigating complex integration scenarios.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Enhancing XYZ’s M&A IT Lifecycle Capabilities
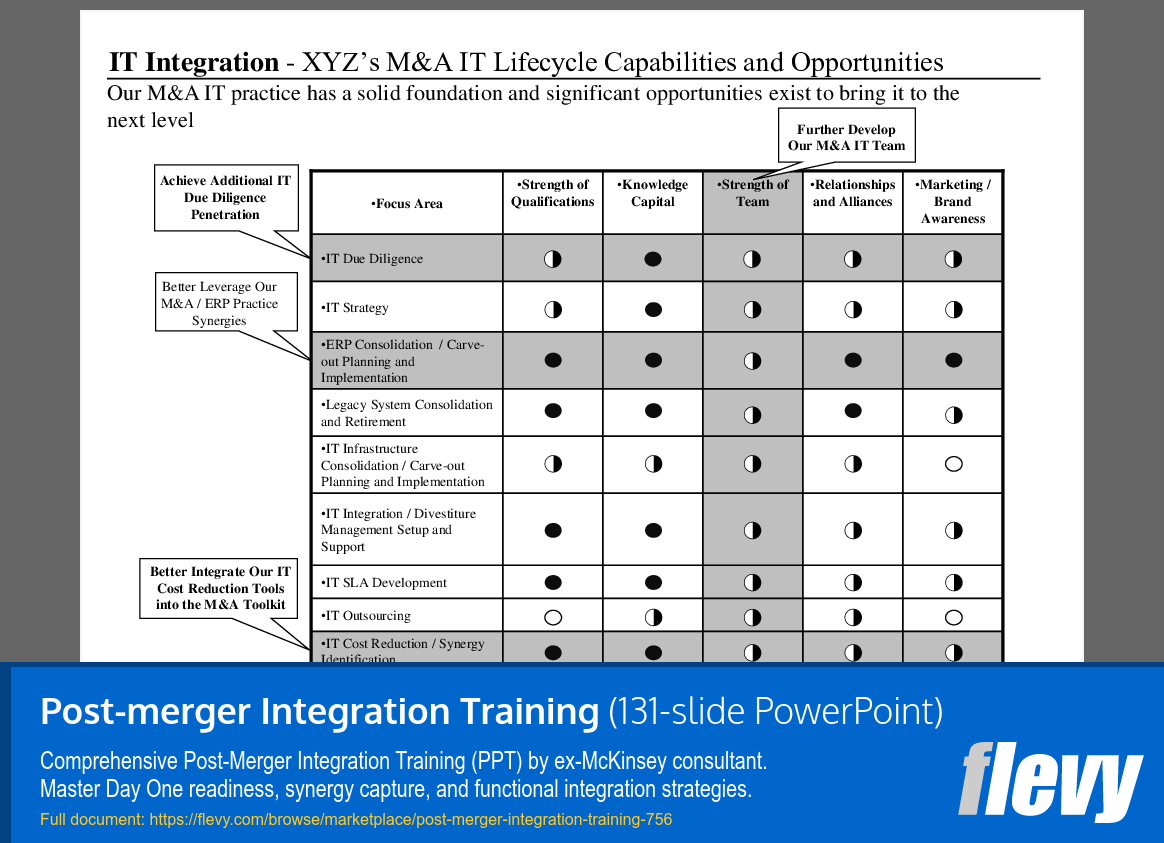
The slide outlines XYZ’s capabilities in the M&A IT lifecycle, focusing on areas that can enhance IT due diligence and strategy. It categorizes essential IT functions and assesses strengths across various domains, revealing a solid foundation in IT Due Diligence while indicating balanced strengths in IT Strategy. This presents a clear picture of where the organization stands in terms of qualifications and knowledge capital.
The next section highlights opportunities for leveraging synergies within the M&A and ERP practices, particularly in ERP and legacy system consolidation. While there are strong qualifications in ERP Consolidation, the varying strengths across functions suggest areas for improvement. The final focus is on integrating IT cost reduction tools into the M&A toolkit, identifying established capabilities, but also significant potential for growth, especially in marketing and brand awareness.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Comprehensive Overview of Finance Integration Services
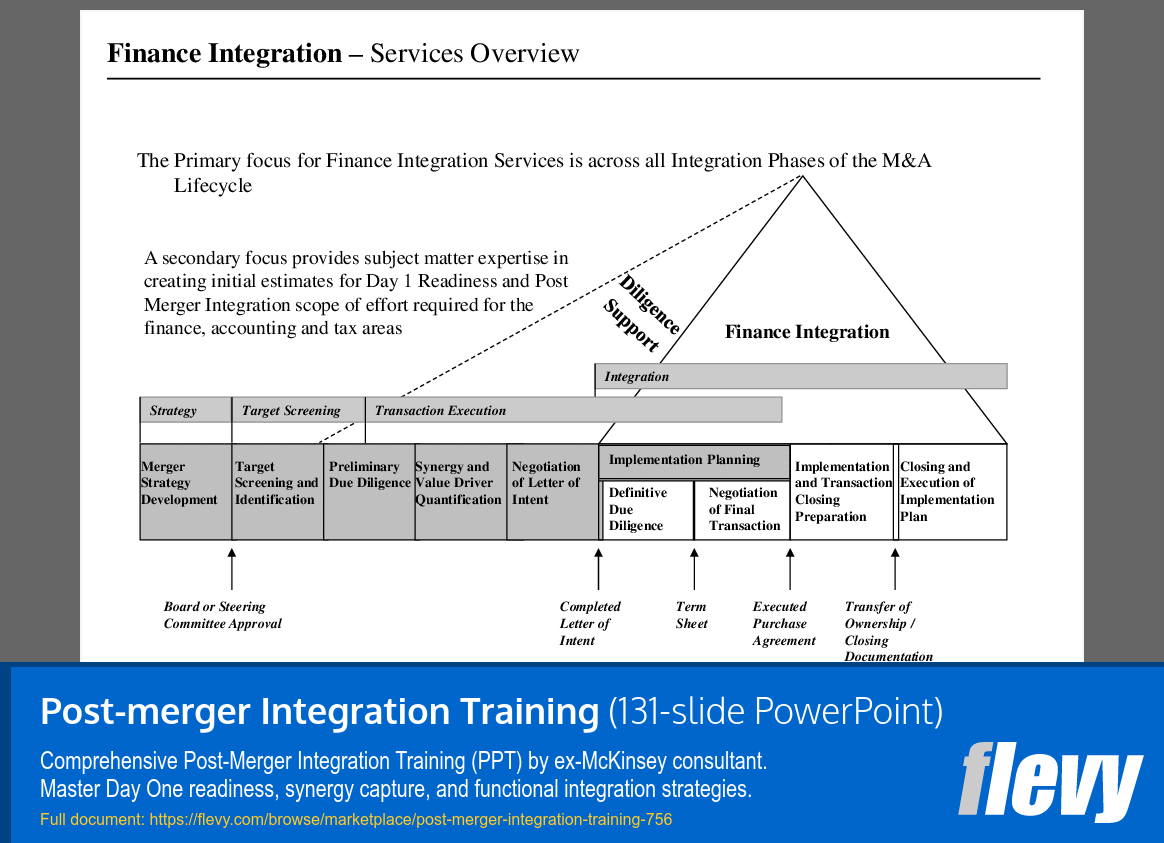
The slide details the Finance Integration Services across the M&A lifecycle, focusing on integration to ensure a smooth transition. It categorizes the process into 3 main areas: Strategy, Target Screening, and Transaction Execution, each containing essential activities for effective finance integration.
Transaction Execution includes critical steps such as “Negotiation of Letter of Intent” and “Definitive Due Diligence,” which formalize agreements and vet financial aspects thoroughly. The slide underscores the importance of “Implementation Planning” to ensure that financial systems are aligned post-merger, ultimately aiming for successful outcomes in M&A activities.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Supply Chain Integration Workflow Overview

The slide presents a structured workflow for integrating supply chains during mergers and acquisitions. It begins with defining data requirements, where both the acquirer and target collaborate to customize templates and finalize data requests. This foundational step is critical for ensuring that subsequent phases are built on accurate and relevant information.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Strategic Opportunity Matrix for Supplier and Product Alignment
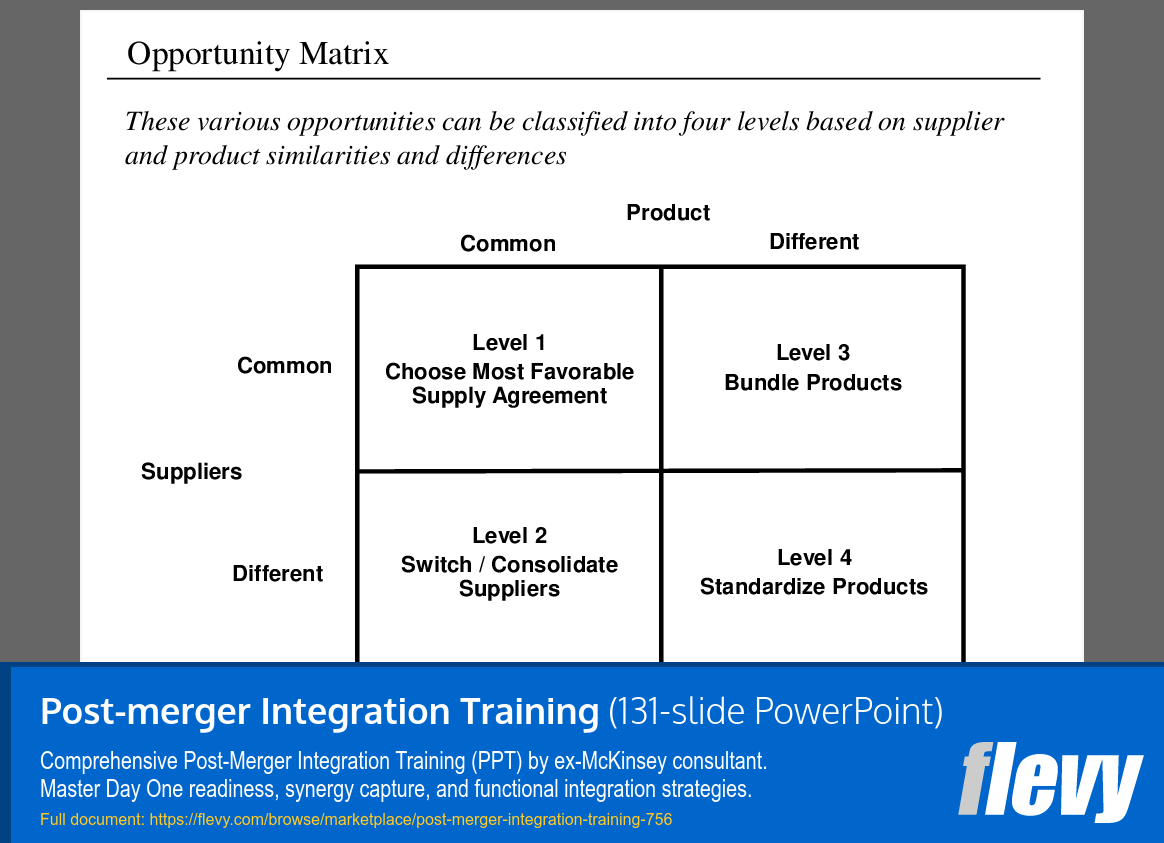
The Opportunity Matrix categorizes various strategic options based on product and supplier similarities and differences. It is divided into 4 levels, each presenting a distinct approach to optimizing supplier relationships and product offerings. This framework aids executives in identifying and prioritizing opportunities effectively.
Level 1 focuses on selecting the most favorable supply agreements for common products and suppliers, aiming to enhance existing relationships. Level 2 encourages switching or consolidating suppliers for common products, but with different suppliers, which can help reduce costs and streamline operations.
In the upper right quadrant, Level 3 emphasizes bundling different products with common suppliers to create integrated solutions that enhance value. Level 4 advocates for standardizing products across diverse suppliers, promoting efficiency and consistency. This matrix serves as a practical tool for decision-making, driving operational effectiveness and market positioning.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Spend Data Templates for Sourcing Optimization
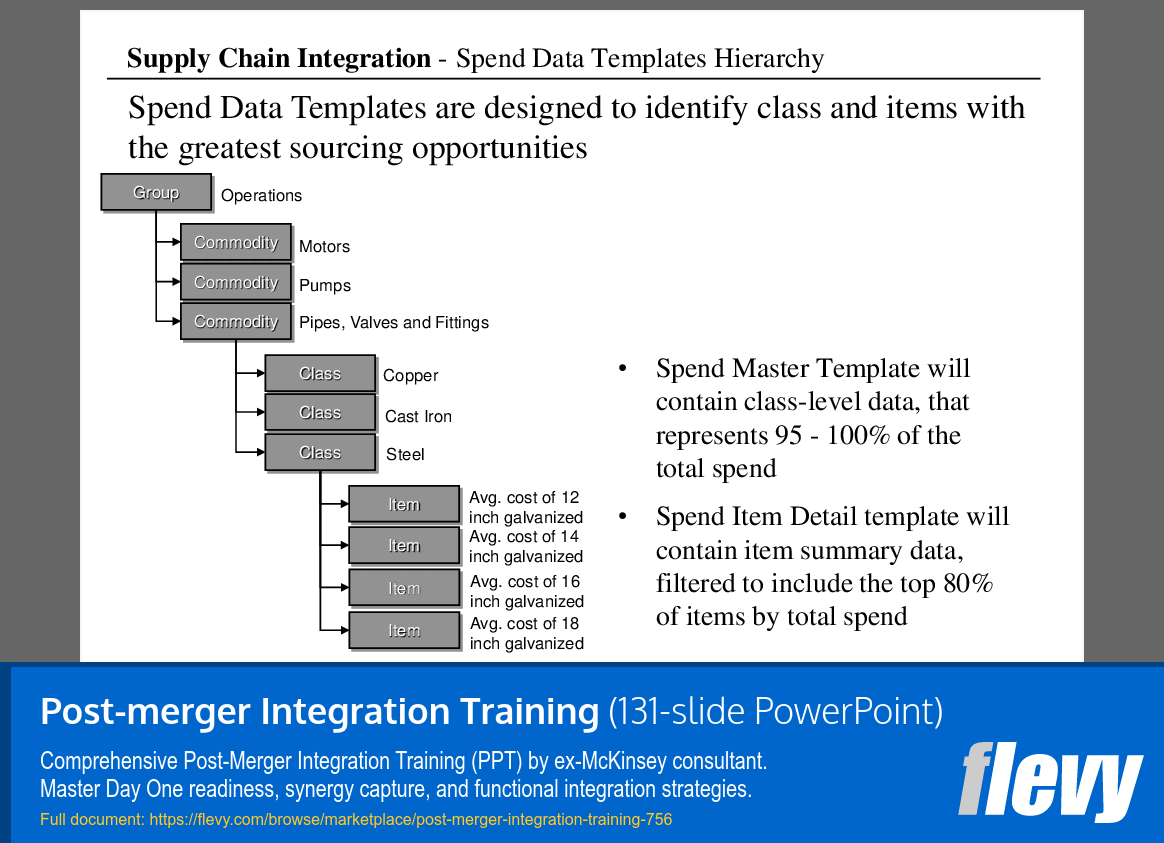
The slide outlines the structure of Spend Data Templates, which are essential for pinpointing sourcing opportunities in supply chain operations. It categorizes data under “Group” labeled as Operations, further dividing it into commodities like Motors, Pumps, and Pipes, Valves, and Fittings. Each commodity is broken down into classes such as Copper, Cast Iron, and Steel, creating a clear hierarchy that supports focused analysis.
Two main templates are highlighted: the Spend Master Template and the Spend Item Detail Template. The Spend Master Template aggregates class-level data, capturing nearly all total spend, which is vital for understanding expenditure trends. The Spend Item Detail Template, on the other hand, summarizes item-level data, emphasizing the top 80% of items by spend, allowing decision-makers to prioritize sourcing effectively.
This slide serves as a practical tool for organizations aiming to improve supply chain efficiency. By utilizing these templates, executives can gain valuable insights into spending behaviors, enabling data-driven decisions that align with their strategic goals.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Detailed Spend Analysis Template for Material Groups

The slide outlines a structured template for analyzing spending across material groups within supply chain integration. It stresses the necessity of detailing each material group to create a comprehensive spend profile, identifying all subcategories down to the lowest level. This approach ensures visibility into spending patterns, which is crucial for informed decision-making.
Key columns in the template include Material Group, Commodity, Description, and Total Spend, among others. This detailed breakdown facilitates targeted analysis, helping to pinpoint significant expenditures and supplier dynamics. For example, the “Operations” material group showcases various commodities and their respective spend amounts, offering insights into their relative importance.
The slide also underscores the importance of comprehensive data sourcing for accurate analysis. By capturing detailed information, organizations can enhance procurement strategies and optimize supplier relationships, ultimately improving operational efficiency. This template serves as a foundational tool for executives aiming to streamline supply chain operations and make strategic financial decisions.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Supply Chain Spend Analysis: Acquirer vs. Target
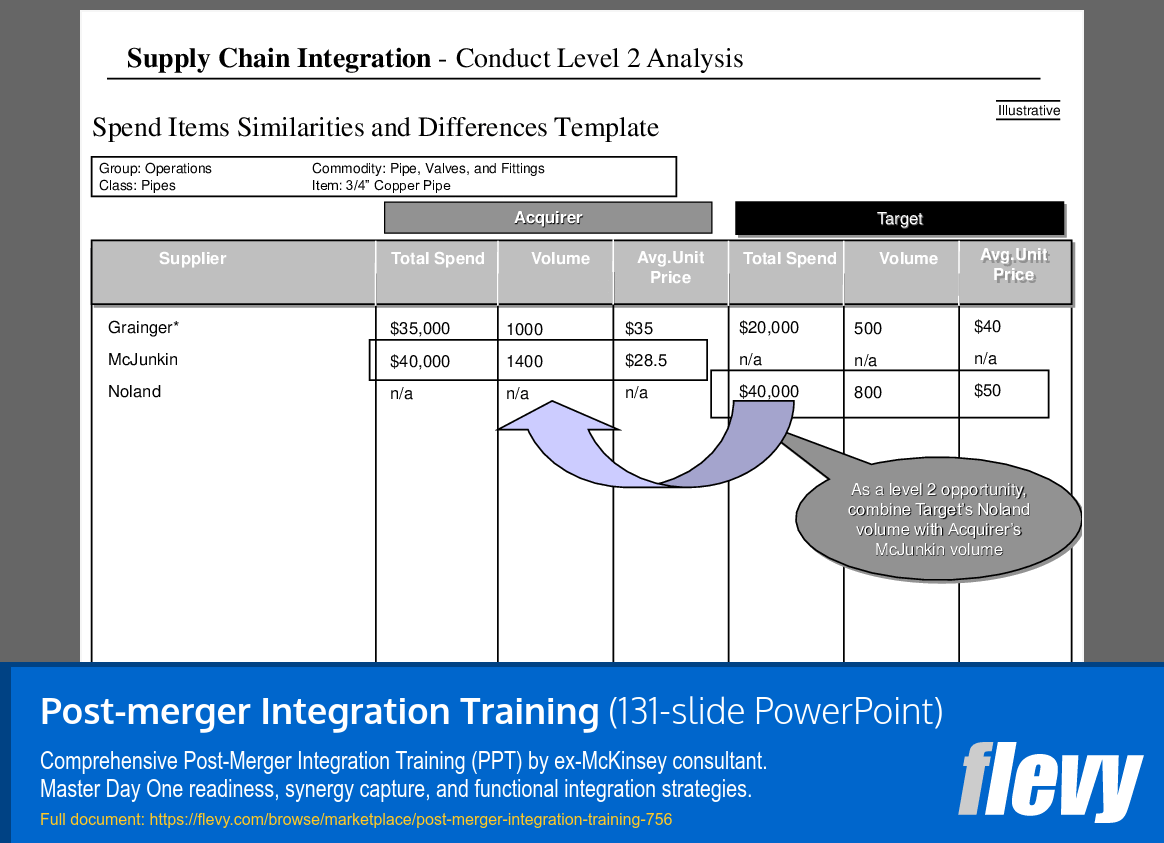
The slide provides a comparative analysis of supply chain expenditures for “3/4” Copper Pipe,” categorizing suppliers into acquirers and targets. Acquirers include Grainger and McJunkin, while the target is Noland. Key metrics such as total spend, volume, and average unit price are presented, revealing distinct spending patterns among the suppliers.
Grainger’s total spend is $35,000 for 1,000 units, translating to an average unit price of $35. McJunkin’s spend is higher at $40,000 for 1,400 units, resulting in a lower average unit price of $28.5. In contrast, Noland’s data shows a total spend of $40,000 for 800 units, with an average unit price of $50, indicating higher costs. The slide suggests a potential synergy by combining Noland’s volume with McJunkin’s, which could enhance cost efficiencies.
This analysis allows decision-makers to quickly grasp spending dynamics, highlighting areas for potential integration and cost savings. It serves as a foundational tool for executives focused on optimizing supply chains in the context of mergers and acquisitions.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Strategic Roll-Out Plan for Supply Chain Integration
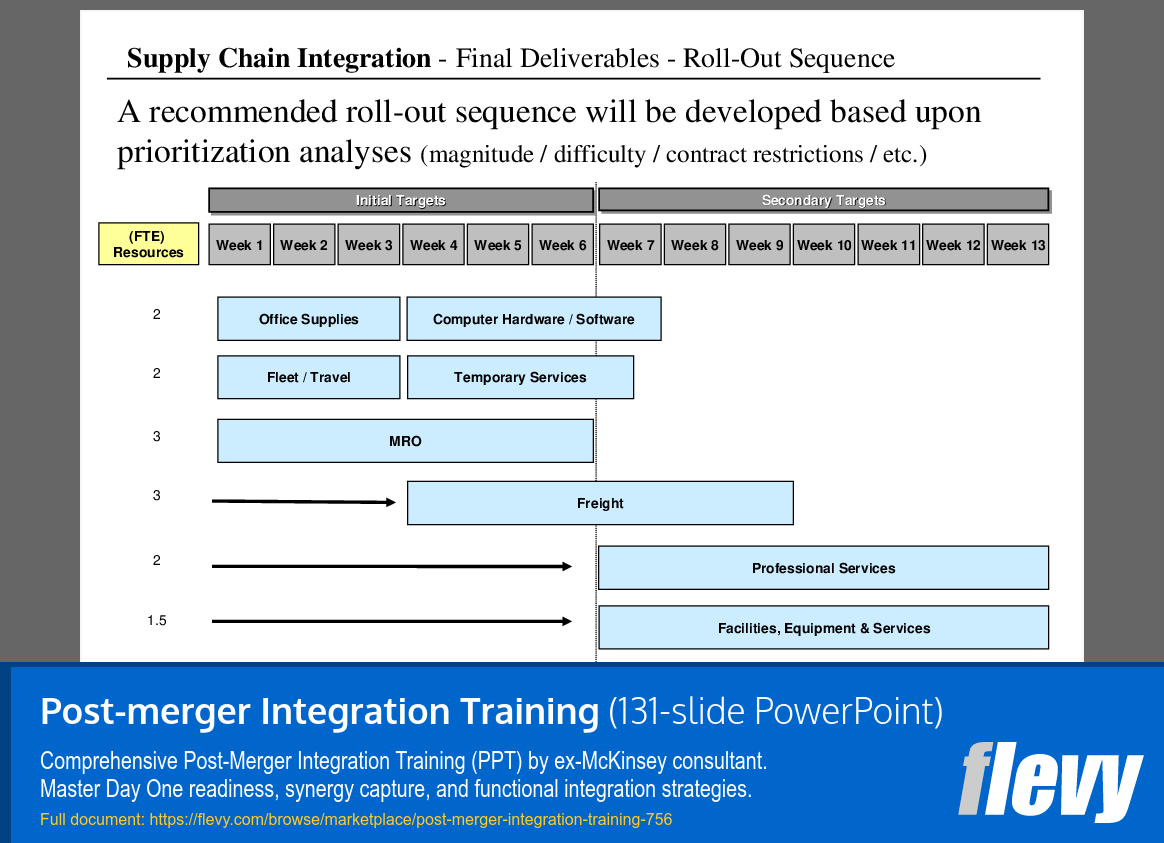
The slide presents a structured plan for supply chain integration, detailing the final deliverables and a phased roll-out sequence over 13 weeks. It categorizes tasks into Initial and Secondary Targets, with specific resource allocations indicated in Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) resources. This approach highlights the prioritization of tasks based on their operational significance and resource needs.
The Initial Targets span Weeks 1 to 6, focusing on essential areas such as Office Supplies, Computer Hardware/Software, and MRO. The Secondary Targets, scheduled from Weeks 7 to 13, shift attention to Freight, Professional Services, and Facilities. This phased strategy allows for a more manageable integration process, addressing critical components first before tackling secondary priorities.
At the top of the slide, a note underscores that the roll-out sequence will be informed by various analyses, including magnitude and contract restrictions. This data-driven methodology aims to ensure an efficient integration process, minimizing disruptions while optimizing resource utilization. The slide serves as a clear roadmap for stakeholders, emphasizing the importance of careful planning in achieving successful integration.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Comprehensive HR Integration Process for Mergers

The slide titled “HR Integration — Overview” outlines the essential phases of post-merger integration, with a focus on human capital. It presents a structured approach that starts with developing a merger strategy and identifying targets, followed by due diligence to assess their viability. The quantification of synergies and value drivers is critical, as it clarifies the potential benefits of the merger before moving into negotiation and execution phases.
Implementation planning is highlighted as a vital stage where detailed strategies for integration are crafted. This includes preparing for the transaction closing, which is crucial for a seamless transition. The slide emphasizes the involvement of various specialists, such as HR strategists and compensation experts, to ensure that human resources are effectively managed throughout the integration process.
The mention of “XYZ Human Capital ‘on the ground’” indicates a hands-on approach to aligning the workforce with new organizational goals. This overview effectively communicates the complexities of HR integration in a merger context, underscoring the need for coordinated efforts across multiple functions to achieve successful outcomes.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Framework for Navigating Organizational Change

The slide outlines a framework for managing organizational change during corporate transformations, such as mergers or acquisitions. It stresses the need to define a clear goal for the desired corporate culture at the outset. A visual curve illustrates the typical emotional and cognitive stages employees experience, starting from “Shock” and moving through “Resistance” to “Understanding.” This progression is crucial for achieving acceptance of the changes.
Initially, organizations encounter negative reactions, which can escalate into resistance against new initiatives. Effective communication and engagement are vital to address this pushback. As employees begin to understand the reasons behind the transformation, they can shift towards enthusiasm and ultimately acceptance, leading to improved organizational performance. The framework serves as a practical guide for executives navigating the complexities of cultural integration during significant change initiatives.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Tailored Corporate Culture Assessment Methodology
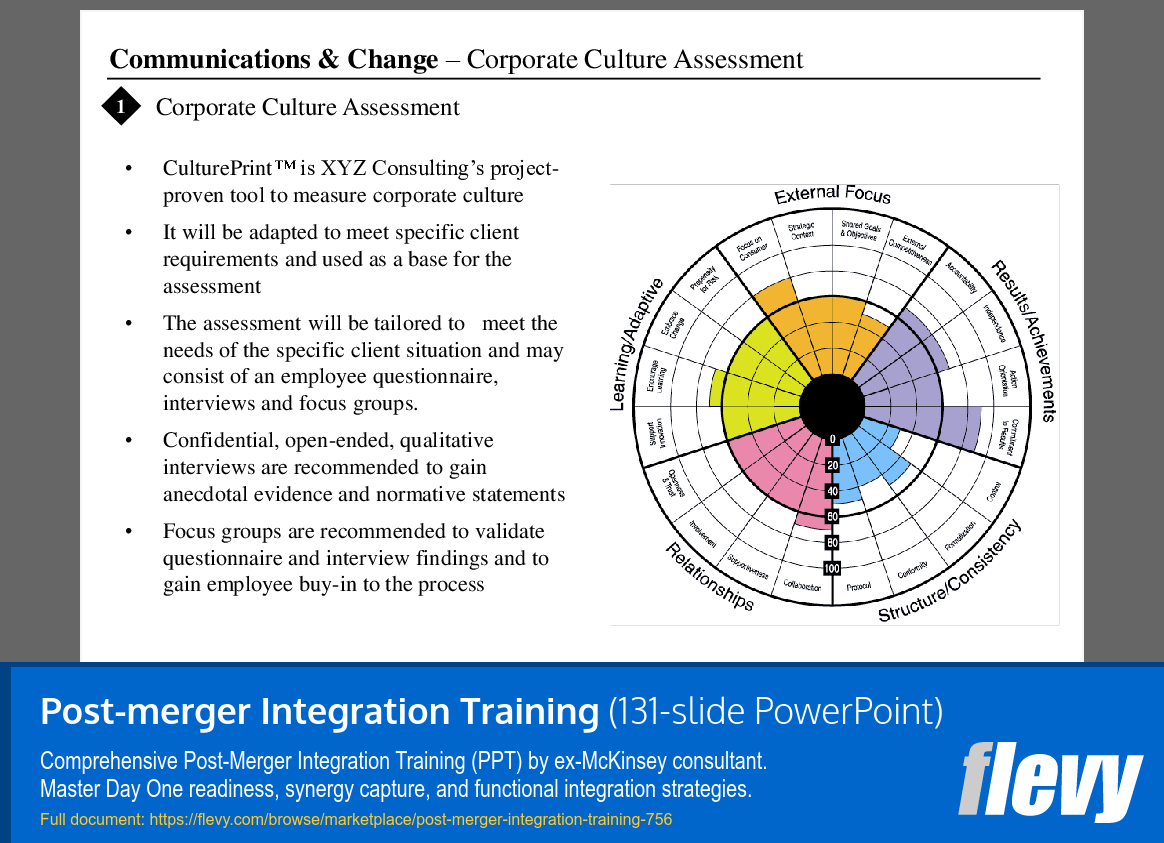
The slide introduces CulturePrint™, a Corporate Culture Assessment tool by XYZ Consulting. This tool is tailored to meet the specific needs of each client, ensuring a customized assessment process that reflects the unique circumstances of the organization. It combines quantitative and qualitative methods to provide a comprehensive view of corporate culture.
The methodology includes an employee questionnaire for quantitative insights, alongside qualitative data gathered from confidential interviews and focus groups. This dual approach captures both statistical measures and personal narratives, enhancing the understanding of the corporate environment. Focus groups are particularly important as they validate findings and foster employee engagement, which is crucial for the success of cultural initiatives.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Strategic Framework for Facilities Cost Reduction
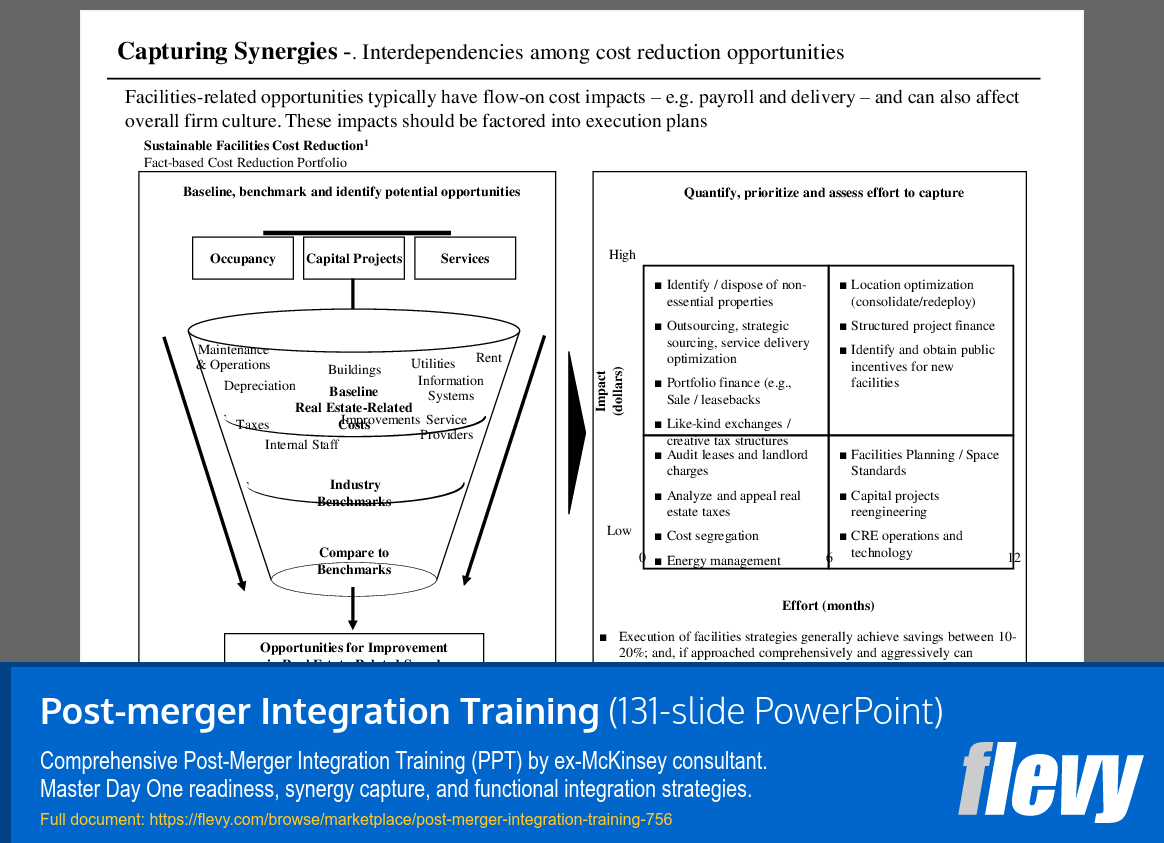
The slide titled “Capturing Synergies — Interdependencies among cost reduction opportunities” presents a framework for identifying facilities-related cost reduction opportunities. It highlights how these opportunities can impact payroll, delivery, and organizational culture, making their integration into execution plans essential. The structured approach categorizes potential initiatives into 3 areas: Occupancy, Capital Projects, and Services, linking them to various cost components like Maintenance & Operations and Depreciation.
The right side of the slide focuses on quantifying and prioritizing these initiatives, using a matrix to plot their expected financial impact against the effort required. High-impact initiatives include disposing of non-essential properties and outsourcing strategies, while lower-impact efforts like energy management still contribute to savings. The slide concludes by suggesting that a comprehensive approach to facilities strategies can yield savings of 10–20%, providing a clear roadmap for organizations aiming to enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Governance Models: Advantages, Challenges, and Evaluation

The slide outlines governance models relevant to organizational integration, focusing on centralized, decentralized, and hybrid approaches. Each model is evaluated based on its benefits and drawbacks, providing clarity for decision-makers navigating these frameworks. Centralized governance can achieve cost efficiencies and simplify management, but may limit flexibility and create disconnects among business units.
Decentralized governance enhances responsiveness to specific business unit needs and allows for tailored solutions. However, it risks inconsistent management practices and can lead to overburdening a few individuals. The hybrid model seeks to combine the strengths of both centralized and decentralized structures, offering flexibility and improved responsiveness while facing challenges in cross-business unit collaboration and early identification of critical issues.
A scorecard at the bottom assesses each governance structure against key criteria such as control and adaptability. This visual tool aids executives in quickly evaluating the effectiveness of each model, essential for optimizing integration processes and driving long-term success.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Assessment of IT Integration in M&A Landscape
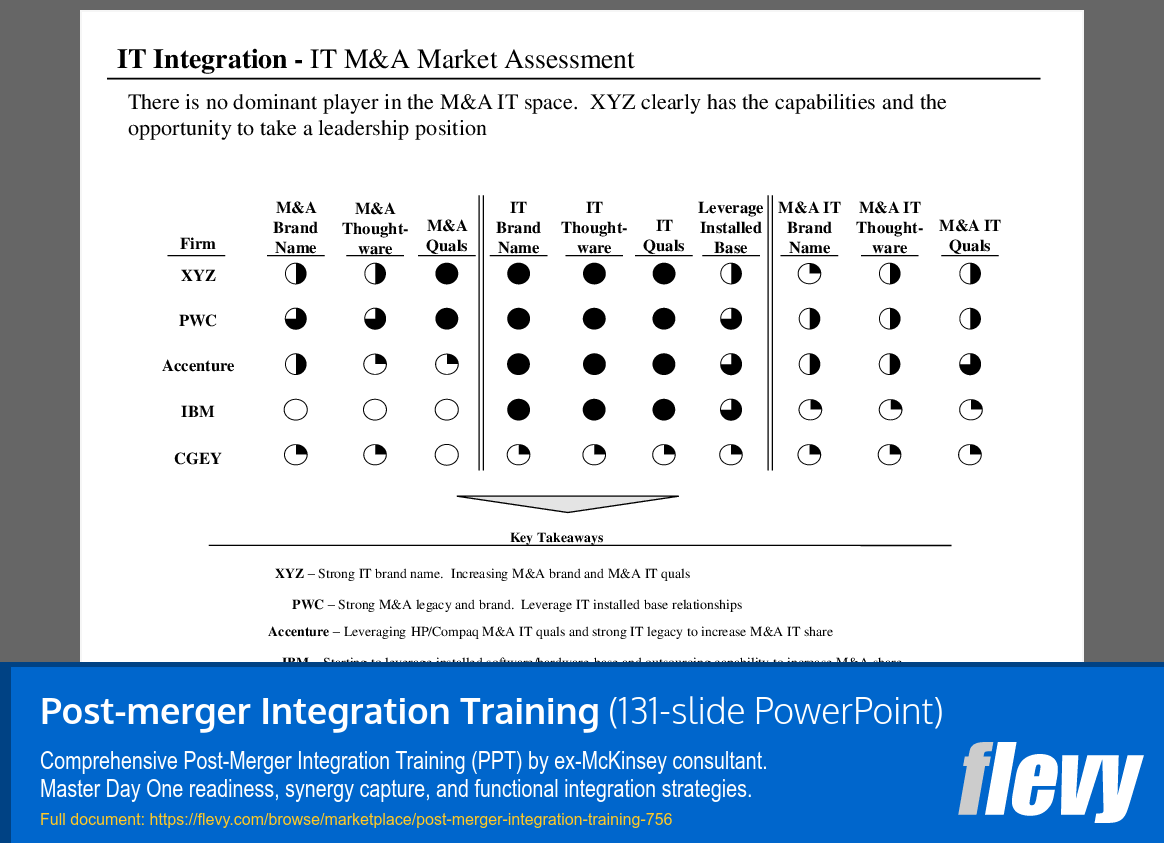
The slide evaluates the IT integration landscape in the M&A sector, revealing a fragmented market without a dominant player. XYZ stands out as a strong contender, showcasing capabilities in M&A branding and IT qualifications. The visual representation uses filled and unfilled circles to depict each firm’s strengths across various dimensions, such as M&A brand name and thought leadership.
Each firm is assessed on its M&A and IT brand names and qualifications. PWC is noted for its strong legacy, while Accenture leverages its HP/Compaq history to enhance its M&A IT presence. Key takeaways highlight XYZ’s robust brand and growing capabilities, alongside IBM’s efforts to improve its installed base and automation capabilities for a stronger M&A position.
