Understanding the Soft Side of Change Management
This article discusses slides taken from a management consulting presentation on the Soft Side of Change Management. You can download the full PPT here.
This presentation focuses on Change Management, emphasizing the importance of addressing the “soft” aspects of organizational transformation. It highlights how understanding the emotional and rational dimensions of change can significantly impact the effectiveness of initiatives aimed at driving change within an organization.
The core framework presented includes 6 key components: Dimensions of Change, Emotional Cycle of Change, Ingredients of Change, Level of Commitment, Phases of Team Building, and Trust Formula. By exploring these elements, leaders can better navigate the complexities of change, identify sources of resistance, and foster a supportive environment that enhances engagement and commitment among team members.
Understanding Support and Resistance in Change Management
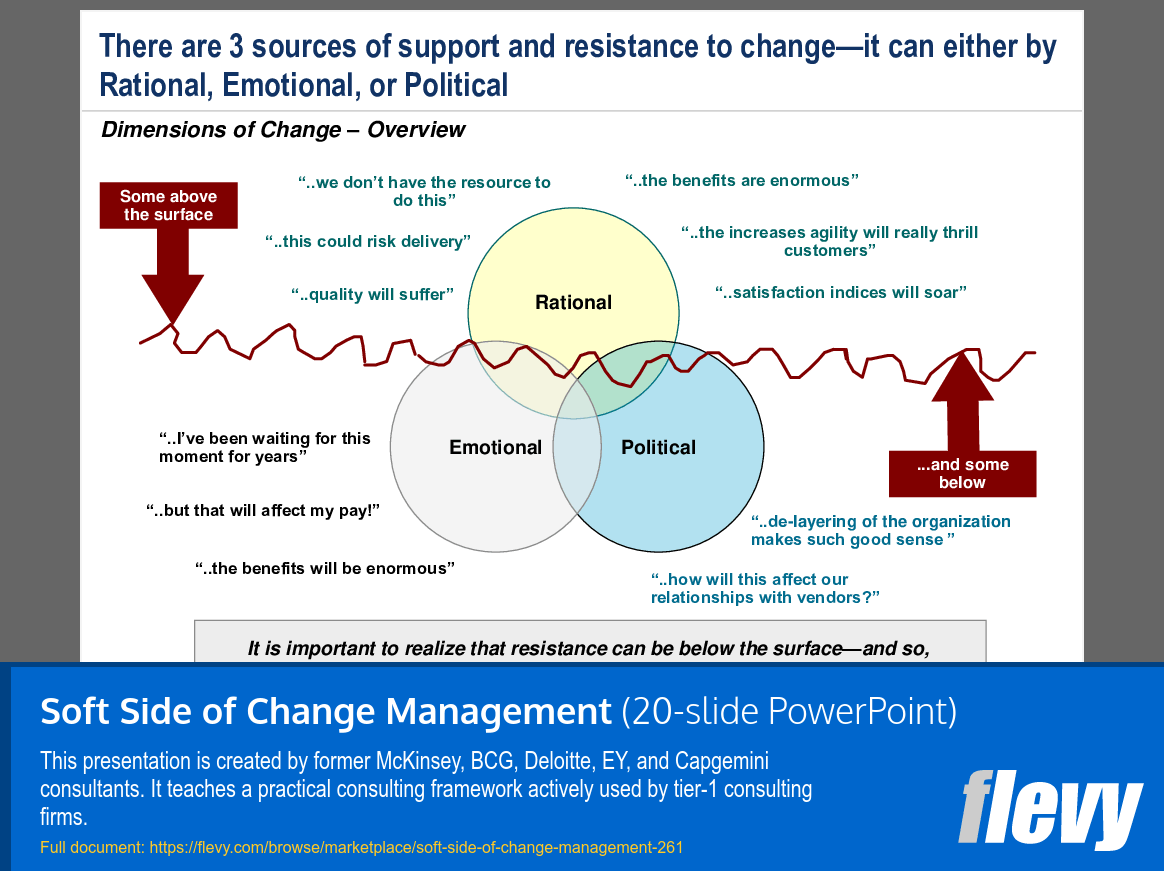
The slide outlines a framework for understanding the sources of support and resistance to organizational change, categorized into 3 dimensions: Rational, Emotional, and Political. The Rational dimension highlights concerns regarding resources, delivery risks, and quality, indicating that stakeholders often assess change through logical evaluations of costs and benefits. The Emotional aspect reveals sentiments of anticipation and personal impact, showing that feelings significantly influence individual responses to change. The Political dimension underscores the role of relationships and power dynamics, suggesting that acceptance or rejection of change can be shaped by interpersonal factors.
This visual representation illustrates that these dimensions can overlap, meaning support or resistance may arise from a combination of rational, emotional, and political factors. The note at the bottom emphasizes that resistance can exist beneath the surface, indicating that not all objections are explicit. This understanding is crucial for leaders as they navigate the complexities of change management.
Ultimately, the slide serves as a reminder that effective change management requires a nuanced approach. Leaders must consider the diverse motivations and concerns of stakeholders to address both visible and hidden sources of resistance, facilitating smoother transitions in their organizations.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Emotional Journey through Organizational Change
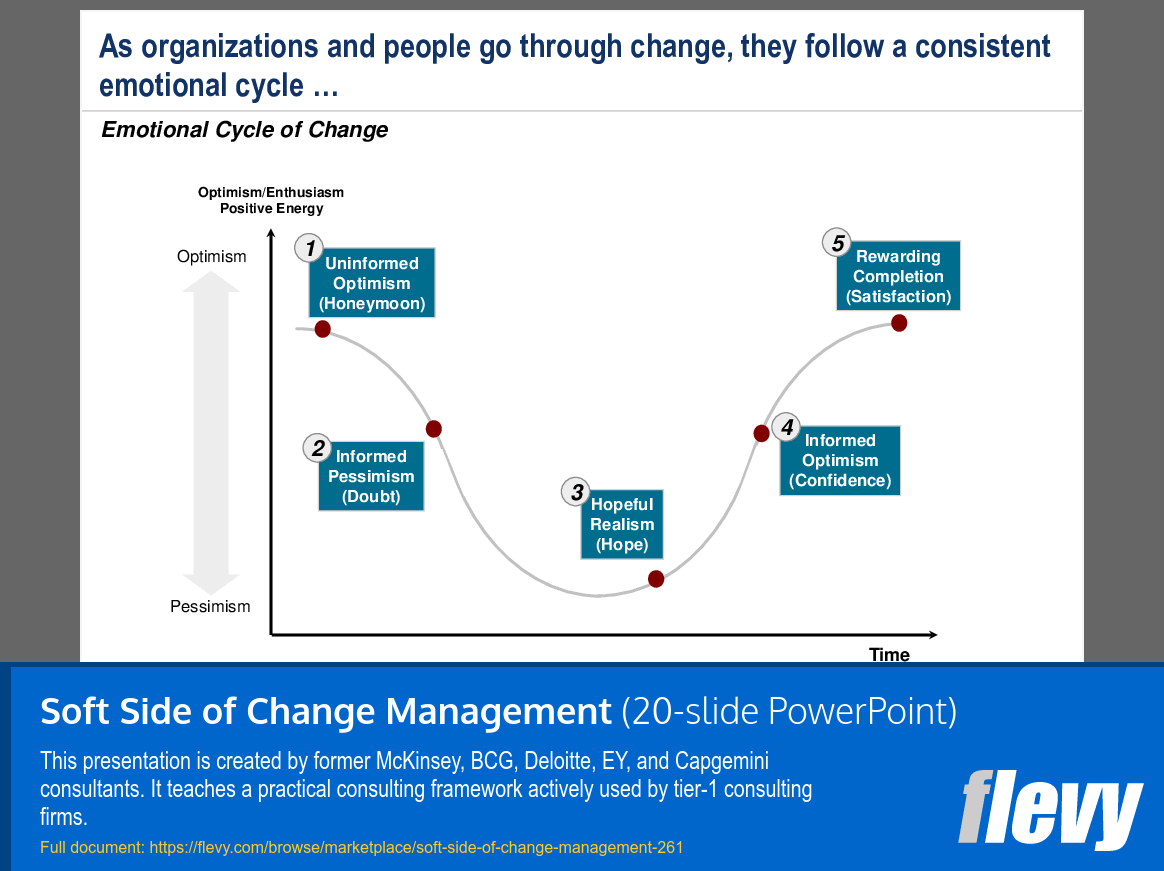
The “Emotional Cycle of Change” illustrates the emotional journey individuals and organizations undergo during periods of change. It starts with “Uninformed Optimism,” where initial excitement is prevalent,, but this phase quickly transitions into “Informed Pessimism,” as the reality of challenges begins to set in. This shift often brings about doubt and uncertainty, highlighting the complexities involved in the change process.
As the cycle progresses, individuals reach “Hopeful Realism,” where a balance between optimism and realism fosters resilience. This is crucial for effective problem-solving. The cycle culminates in “Rewarding Completion,” where individuals experience satisfaction and a sense of achievement after successfully navigating the change. Understanding this cycle is vital for leaders to provide necessary support and communication at each stage, ensuring a smoother transition.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Essential Components for Effective Change Management
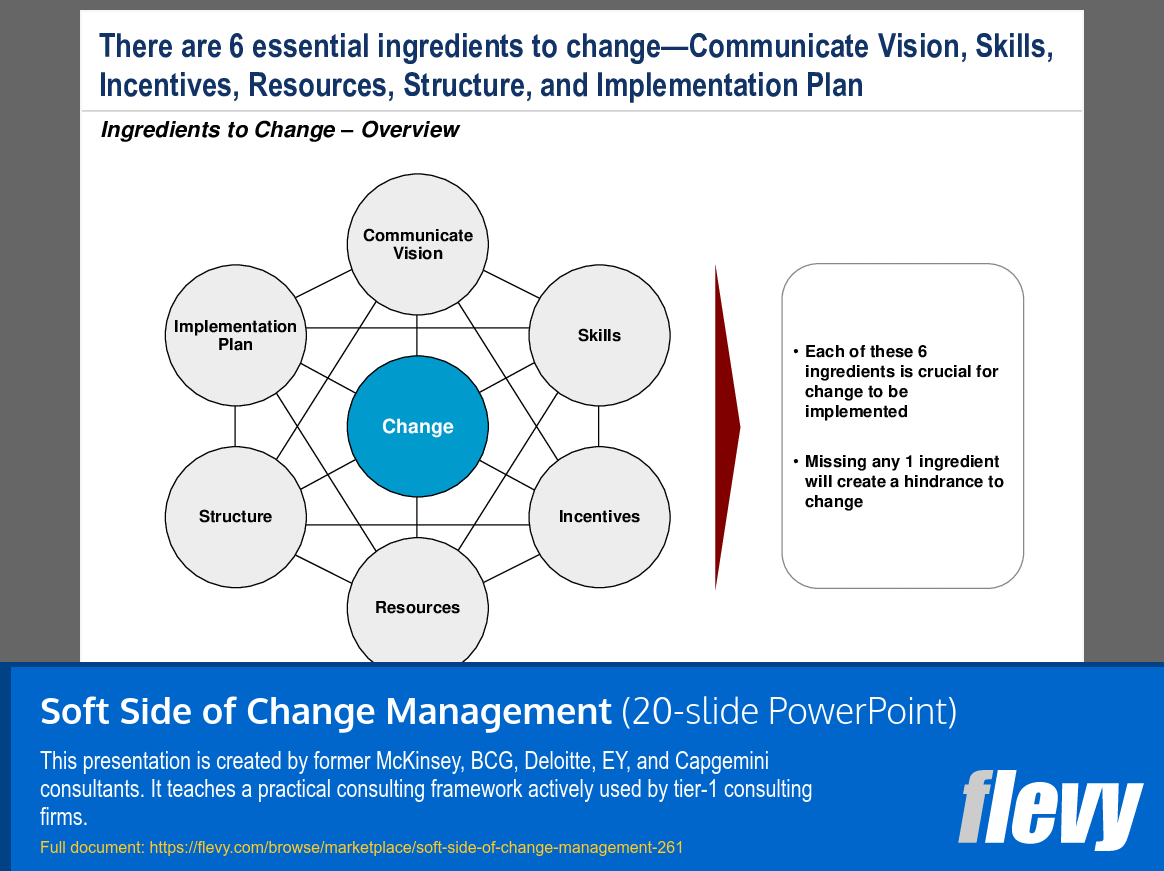
The slide presents 6 key components essential for effective change management, centered around the concept of “Change.” These components — Communicate Vision, Skills, Incentives, Resources, Structure, and Implementation Plan — are interconnected, emphasizing that they must function together to facilitate successful organizational change. Each element is critical, and the absence of any one can significantly hinder the change process.
This framework underscores that change is complex and not a straightforward journey. Executives should thoroughly evaluate each component before initiating any change initiative. This approach can lead to better decision-making and more strategic resource allocation, ultimately enhancing the likelihood of successful transformations.
Read a more in-depth analysis of this PPT slide here.
Commitment Progression: From Awareness to Internalization
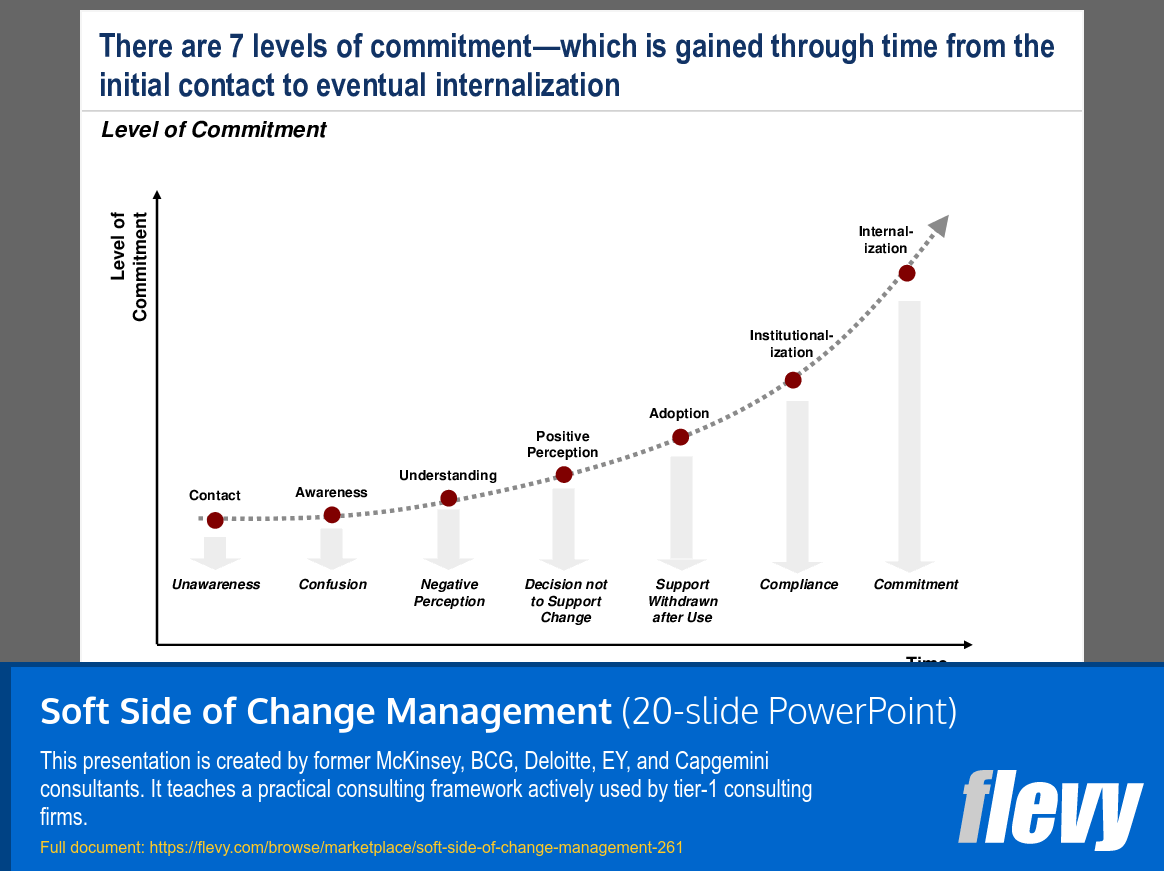
The slide presents a framework illustrating 7 levels of commitment that individuals or organizations experience over time, from initial contact to full internalization of a change. The vertical axis indicates the “Level of Commitment,” while the horizontal axis represents “Time.” It starts with “Unawareness,” where there is no knowledge of the change, progressing through stages like “Contact,” “Awareness,” and “Understanding.” However, this understanding can lead to “Confusion,” which may impede commitment.
As individuals move through these levels, they may encounter “Negative Perception,” which can stall progress. If they overcome this, they reach “Positive Perception,” recognizing the benefits of the change. The framework culminates in “Commitment,” where individuals fully internalize and actively support the change. This progression highlights that achieving commitment is a gradual process, requiring time and multiple interactions to evolve from mere awareness to deep acceptance.
